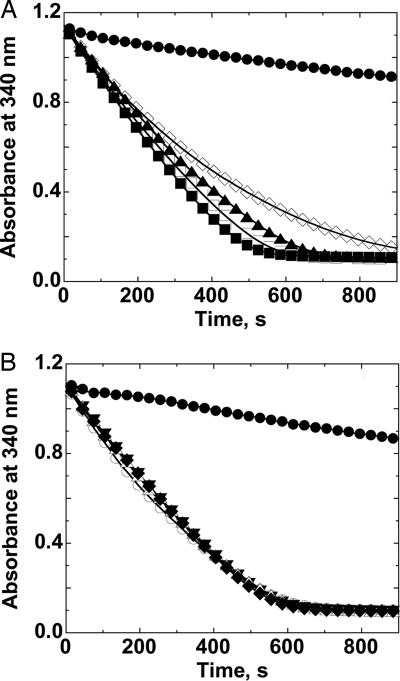
Fig. 4.
AhpC shows a susceptibility to inactivation by hydrogen peroxide and ethyl hydroperoxide, but not to t-butyl hydroperoxide and cumene hydroperoxide. NADPH oxidation was measured (by monitoring loss of 340-nm absorbance) at 25°C in the presence of 50 mM Hepes-NaOH, pH 7.0, with 1 mM EDTA and 0.1 M ammonium sulfate, and with 80 nM Trx reductase, 2.5 μM Trx, 6 μM AhpC and ethyl hydroperoxide (A) at 0 mM (●), 1 mM (■), 5 mM (□), 10 mM (▴), and 30 mM (◇). The same conditions were used to examine overoxidation with t-butyl hydroperoxide (B), except that concentrations of this substrate were at 0 mM (●), 2 mM (▾), 10 mM (▵), 20 mM (◆), and 60 mM (○). Results with hydrogen peroxide were very similar to those with ethyl hydroperoxide (A), whereas results with cumene hydroperoxide were quite similar to those with t-butyl hydroperoxide (B), except for issues with lower solubility and DMSO effects in the latter case.