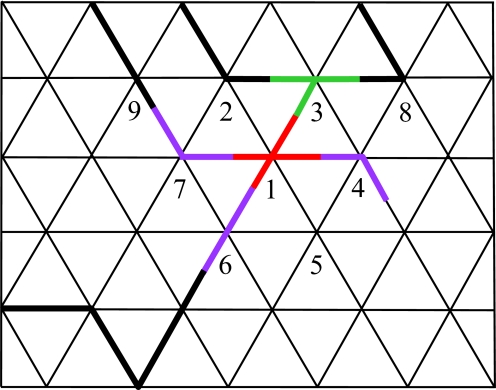
Fig. 2.
Correspondence of the polymer networks to n = 0 spin systems. The solid lines denote boundaries between the meaning islands induced by the code on the dual graph (Fig. 1 Right). In the spin model, to each edge a spin Sij is assigned. Each vertex i contributes to the spin Hamiltonian HS a factor hi, which accounts for all possible edge occupancies around this vertex. By the construction hi (Eq. 5), if a vertex is occupied then at least two of the adjacent edges are occupied. In the present example, a four-junction at vertex 1 (red), which corresponds to a factor a1b13S13b14S14b16S16b17S17, connects to three linear elements (magenta), e.g., a7b71S71b79S79, and one three-junction (green), a3b31S31b32S32b38S38. The corresponding contribution to the spin partition function ZS is an average over all of the spin orientations. This contribution does not vanish because each spin appears exactly twice in the product because Sij appears exactly once in both edge configurations of i and j. The weight of this contribution is the product of the bij-s and ai-s for each edge and vertex in the product.