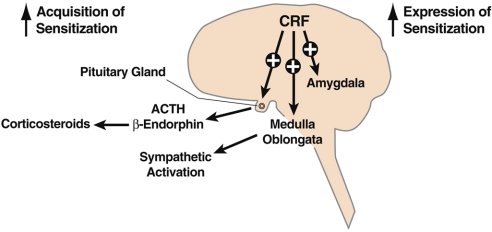
Fig. 1.
CNS actions relevant to alcohol-induced psychomotor sensitization. CRF is a neuropeptide in the brain that controls autonomic, hormonal, and behavioral responses to stressors. New data show that CRF also has a role in the neuroplasticity associated with addiction. The present study extends the role of CRF to the psychomotor sensitization associated with repeated administration of alcohol. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses produced by CRF appear to be more involved in the acquisition of sensitization, whereas extrahypothalamic CRF systems, likely to be in structures such as the amygdala, appear to be important for the expression of sensitization. These results, combined with previous studies on the role of CRF in the development of alcohol dependence, suggest a key role for CRF in the neuroplasticity associated with addiction.