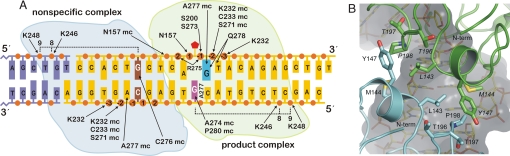
Fig. 2.
Schematic overview of the enzyme–DNA interactions and the dimer interface. (A) The 22-bp DNA is yellow with phosphates shown as orange circles. The adjoining DNA fragment (purple) shows contacts with K246 and K248 from the NS subunit. The arrows represent hydrogen bonds involving side-chain or main-chain (mc) atoms of the enzyme. In the product complex, the flipped abasic nucleotide (THF) is a red pentagon, the “opposing G” is magenta, and the “3′-G” is cyan. A277 intercalates the complementary strand, disrupting base-stacking interactions between the opposing G and its 5′ neighbor. Contacts involving N157, S273, and A274 for hTDGcat are topologically conserved with contacts in the eMUG product complex (17), and the N157, K232, S271, and S273 contacts are conserved with those in the UDG product complex (29). (B) Close-up view of the dimer interface, with the G·THF-bound subunit in green and the nonspecific subunit in cyan. The N termini of each subunit (T123) are indicated.