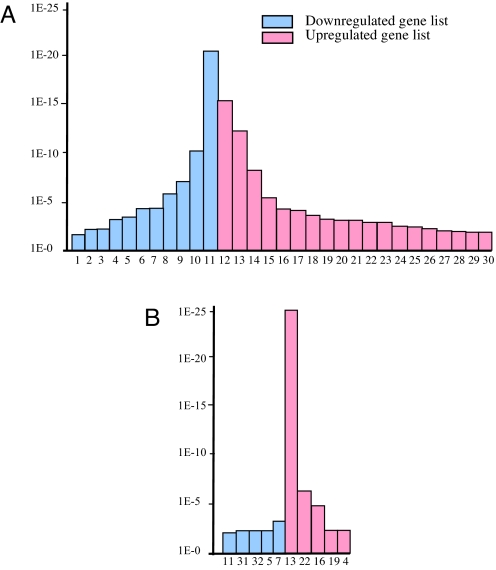
Fig. 1.
Pathway involvement of BEN- (A) and TFII-I- (B) modulated genes. y axis, P values for significance of enrichment; x axis, KEGG pathway terms, listed as follows: 1, arachidonic acid metabolism; 2, nitrogen metabolism; 3, hedgehog signaling pathway; 4, type I diabetes mellitus; 5, calcium signaling pathway; 6, maturity-onset diabetes of the young; 7, cell adhesion molecules (CAMS); 8, hematopoietic cell lineage; 9, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction; 10, complement and coagulation cascades; 11, neuroactive ligand–receptor interaction; 12, cell cycle; 13, ribosome; 14, proteasome; 15, focal adhesion; 16, apoptosis; 17, insulin signaling pathway; 18, antigen processing and presentation; 19, adherens junction; 20, MAPK signaling pathway; 21, ATP synthesis; 22, gap junction; 23, citrate cycle (tricarboxylic acid); 24, oxidative phosphorylation; 25, TGFβ signaling pathway; 26, reductive carboxylate cycle (CO2 fixation); 27, neurodegenerative disorders; 28, FcεRI signaling pathway; 29, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway; 30, dorso–ventral axis formation; 31, leukocyte transendothelial migration; 32, cysteine metabolism.