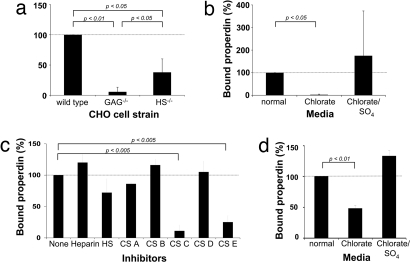
Fig. 4.
Sulfated GAGs mediate the binding of properdin to apoptotic T cells. (a) Wild-type, GAG-deficient, and HS-deficient CHO cells were incubated with purified properdin and bound properdin measured via FACS. (b) Wild-type CHO cells were cultured in chlorate-containing media to prevent sulfation of GAGs and then analyzed for their ability to bind properdin. The addition of sodium sulfate (SO4) reversed the inhibitory effect of chlorate on GAG sulfation. (c) Apoptotic T cells were preincubated at 20 μg/ml in buffer/media with heparin (predominantly alternating IdoA2S-GlnNS6S), HS (an undersulfated form of heparin), CS-A (chondroitin sulfate-A; GlcA-GalNAc4S), CS-B (dermatan sulfate; IdoA-GalNAc), CS-C (GlcA-GalNAc6S), CS-D (GlcA2S-GalNAc6S), or CS-E (GlcA-GalNAc4, 6S). Purified properdin was then added to all samples, and properdin deposition on the T cell surface was assessed. (d) T cells were activated in normal media or media containing chlorate or chlorate and SO4, and deposition of purified properdin was measured after apoptosis induction. All values shown are the mean ± SD values derived from a minimum of three separate experiments.