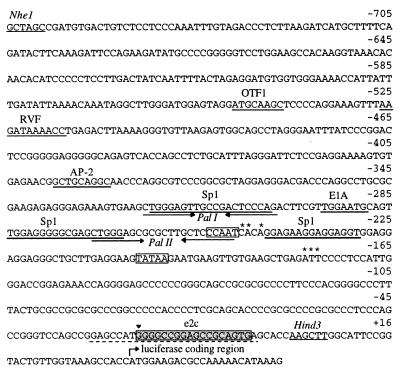
Figure 1.
Nucleotide sequence of the human erbB-2 promoter fragment used in these studies. Nucleotide positions −758 to −1 relative to the ATG initiation codon are shown, with known transcription factor binding sites (16) underlined. Sp1 binding sites are marked as mapped by DNase footprinting (32). The two palindromic sequences Pal I and II bound by RBPJκ (11) are marked by inverted arrows. CCAAT and TATAA sequences are boxed. The major transcription initiation sites (19) are indicated by asterisks. The zinc finger target sequence e2c is underlain with a gray box. The short stretch of sequence identity between human, rat, and mouse genes is indicated by a dashed underline. Restriction sites used for cloning of the promoter fragment are indicated. The arrowhead at position −24 denotes the 3′ end of an erbB-2 control promoter fragment lacking the zinc finger target sequence e2c.