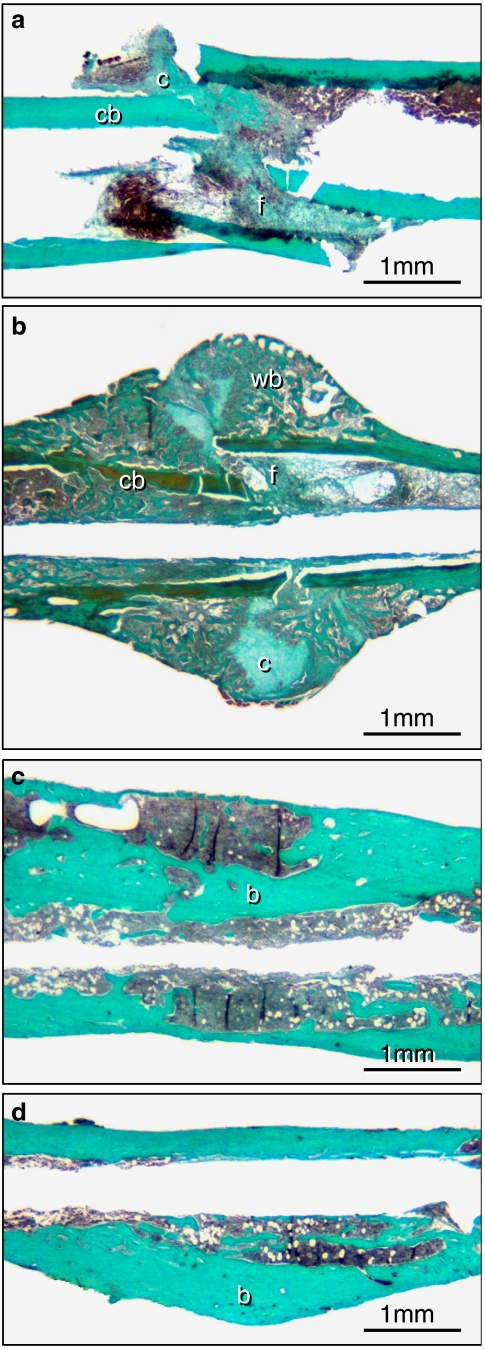
Figure 2.
Longitudinal sections of the callus of femora at 2 (a and b) and 5 (c and d) weeks of fracture healing stained according to the trichrome method. a and c show the callus of rapamycin-treated animals, b and d that of controls. At 2 weeks, callus consisted of cartilaginous (c) and fibrous (f) tissue as well as of cortical (cb) and newly woven bone (wb). Note that at 2 weeks callus is dominated by newly woven bone in the control animal (b), whereas callus formation is significantly diminished after rapamycin treatment (a). At 5 weeks post-fracture cartilaginous and fibrous tissue disappeared completely in both groups. A distinction between newly maturing bone (b) and old surrounding bone (b) is not evident.