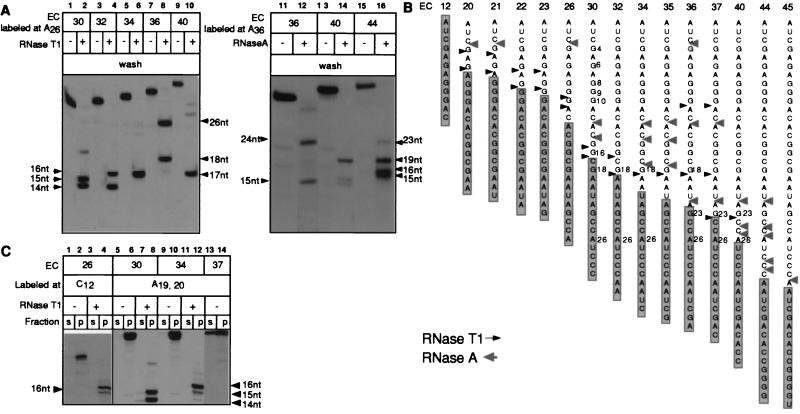
Figure 3.
Cleavage of the RNAs with RNases T1 and A in a number of consecutive ECs and their effect on EC stability. (A) The indicated ECs were digested with 5,000 units/ml of RNase T1 (Left) or with 5 μg/ml RNase A (Right), washed, and then combined with phenol. (B) Summary of RNase footprinting data obtained for the T7A1 transcription unit. Arrows show the cleavage sites introduced in the RNAs at high doses of RNases T1 and A, when the cleavage was stopped either by adding nondenaturing inhibitors or by washing off the RNases. The information shown is based on 3–5 separate experiments performed with RNAs labeled at various positions. The shaded rectangles represent the minimal 14-nt segment of the RNAs protected by RNAP in the intact ECs. (C) The indicated ECs, either intact or treated with RNase T1 and washed as described in A, were incubated in TB containing 300 mM KCl before separating the samples into supernatant and pellet (s and p).