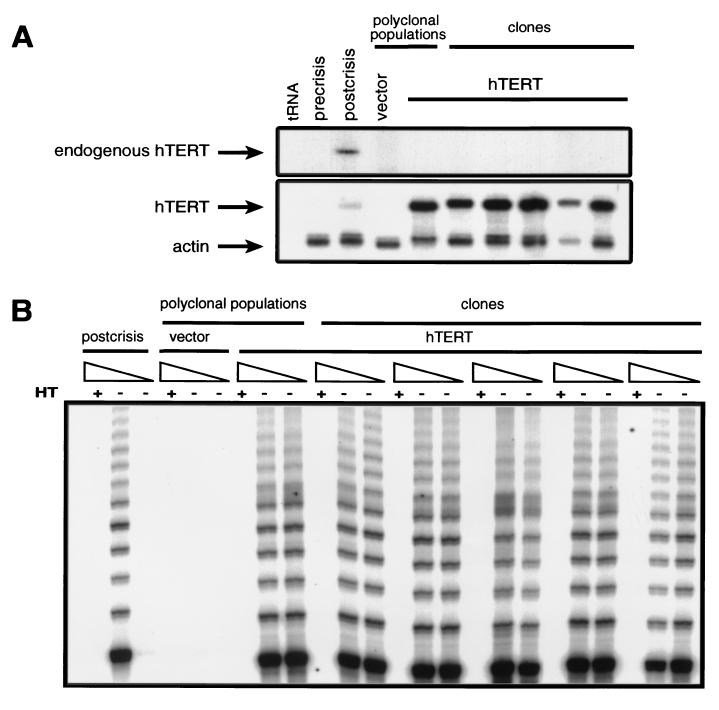
Figure 1.
hTERT expression confers telomerase activity in transformed human cells. (A) T-Ag-transformed HEK cells were infected with control or hTERT-expressing retroviruses. Total RNA (40 μg) was isolated from the resulting polyclonal populations and clonal isolates and assayed for hTERT expression by an RNase protection assay using antisense probes specific for the 3′ untranslated portion region of hTERT (endogenous) or the terminal 275 bp of the hTERT cDNA (hTERT). The latter probe protects identical length RNA fragments when hybridized with both endogenous and ectopic hTERT mRNA. Yeast tRNA and a human β-actin probe demonstrate the specificity of the probe and the presence of equal amounts of RNA, respectively. (B) Cytosolic cellular extracts (0.2 or 0.02 μg) prepared from the parental line postcrisis, control, or hTERT-infected populations, or hTERT-infected clonal isolates were assayed for telomerase activity. As a negative control, 2 μg of all extracts tested was heat treated (HT) to inactivate telomerase before telomere repeat amplification protocol assay.