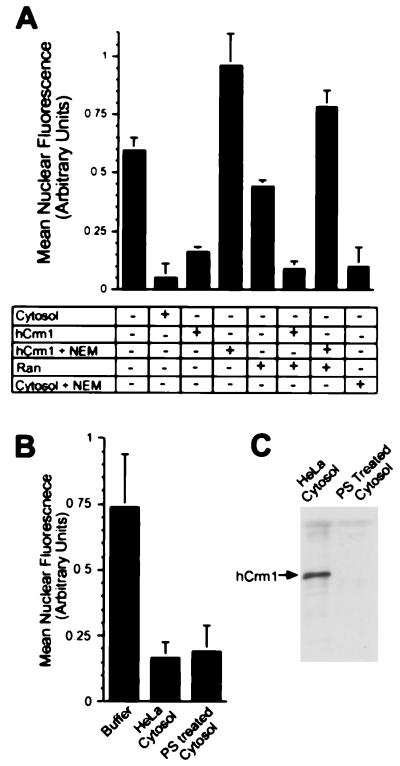
Figure 4.
Analysis of the cytosolic factors that mediate PKI export in permeabilized cells. (A) Addition of HeLa cytosol (3 mg/ml) or purified Crm1 (30 μg/ml) strongly stimulates nuclear export. NEM treatment of Crm1 inactivates its export activity. In contrast, NEM treatment of cytosol did not inactivate its export activity, indicating that cytosol contains an export-promoting activity that is insensitive to sulfhydryl alkylation and therefore different from Crm1. The higher nuclear signal in samples containing NEM-treated Crm1 was observed in three separate experiments. It suggests that the chemically modified Crm1 exerts a slight dominant-negative effect by reducing export promoted by factors remaining within the permeabilized cell. Note that the human Crm1 and cytosol samples in this experiment were mock-treated with NEM (see Materials and Methods). In this experiment, a 20% reduction in nuclear bPKI/FITC-STV-NLS was observed after the addition of Ran (100 μg/ml). In most experiments, however, the addition of Ran had no effect on export, indicating it is not a major rate-limiting factor in our assay. Note that this concentration of Ran corresponds to at least a 5-fold excess over the concentration of Ran present in HeLa cell cytosol used in our export assays. (B) Cytosol depleted of Crm1 stimulates PKI export in permeabilized cells. HeLa cytosol was depleted of Crm1 by incubation with phenyl-Sepharose, and the unbound fraction (PS cytosol; 3 mg/ml) was tested in the PKI export assay. (C) The depletion of Crm1 from cytosol was demonstrated by immunoblotting using an anti-peptide Crm1 antibody.