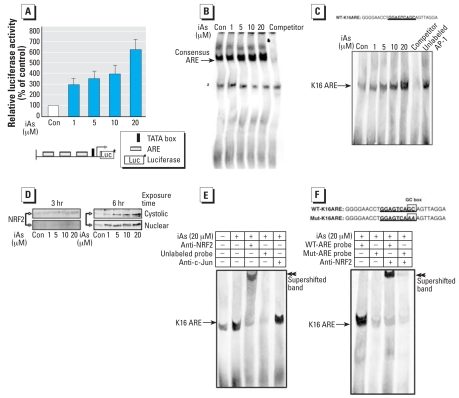
Figure 4.
iAs potently stimulates the ARE and induces production and translocation of NRF2 into the nucleus of HaCaT cells. Abbreviations: +, presence; –, absence; Con, control. (A) Effect of iAs on ARE-driven promoter activity determined using cotransfection of the p3xARE/Luc reporter gene construct (shown schematically in the lower panel), containing three copies of the ARE, into HaCaT cells with the pRL-TK vector encoding Renilla luciferase. See “Materials and Methods” for details. Values shown indicate the ratio of the luciferase activities in untreated cells and in cells treated with 20 μM iAs for 6 hr; luciferase activity with no treatment was defined as 100%. Values represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments, each run in triplicate. (B) Results of EMSA analyses performed using iAs-stimulated nuclear extracts and a biotinylated consensus ARE probe. The arrow indicates the consensus ARE probe-nuclear protein band shifts; an unlabeled consensus ARE probe was used as a competitor oligo. (C) EMSA of nuclear extracts prepared from cells treated with iAs for 6 hr using a biotinylated WT-K16ARE probe (5′-GGGGAACCTGGAGTCAGCAGTTAGGA-3′, with the wild-type ARE sequence found in the K16 promoter from –157 to –132 bp underlined). An unlabeled WT-K16ARE probe was used as a competitor. To determine the binding specificity of ARE, an unlabeled AP-1 oligonucleotide was added to the iAs-treated nuclear extracts before the addition of the labeled WT-K16ARE probe. The arrow indicates shifted K16ARE-nuclear protein complexes. (D) Nuclear accumulation of NRF2 stimulated by iAs in HaCaT cells maintained in serum-free medium for 24 hr and then treated with iAs for 3 or 6 hr. Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were then prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis using polyclonal NRF2 antibodies; results shown represent three independent experiments. (E) Regulation of the ARE site within the K16 gene promoter after iAs treatment. The WT-K16ARE probe was incubated with nuclear extracts prepared from cells cultured in the absence (–) or presence (+) of 20 μM iAs for 6 hr. For supershift EMSA analysis, the nuclear extracts were incubated with either an anti-NRF2 or anti-c-Jun antibody before the addition of labeled probe. The binding specificity was confirmed by the addition of excess unlabeled WT-K16ARE probe. The arrow indicates shifted complexes, and double arrowheads indicate supershifted K16ARE-NRF2 complexes. (F) In a similar experiment to the one shown in (E), either a WT-K16ARE or Mut-K16ARE probe was incubated with nuclear extracts of cells cultured in the presence of 20 μM iAs for 6 hr. The GC box of Mut-K16ARE was substituted with AA as indicated. Anti-NRF2 antibody was used in the supershift assays. The arrows and double arrowheads indicate shifted and supershifted complexes, respectively.
aNonspecific band.