Abstract
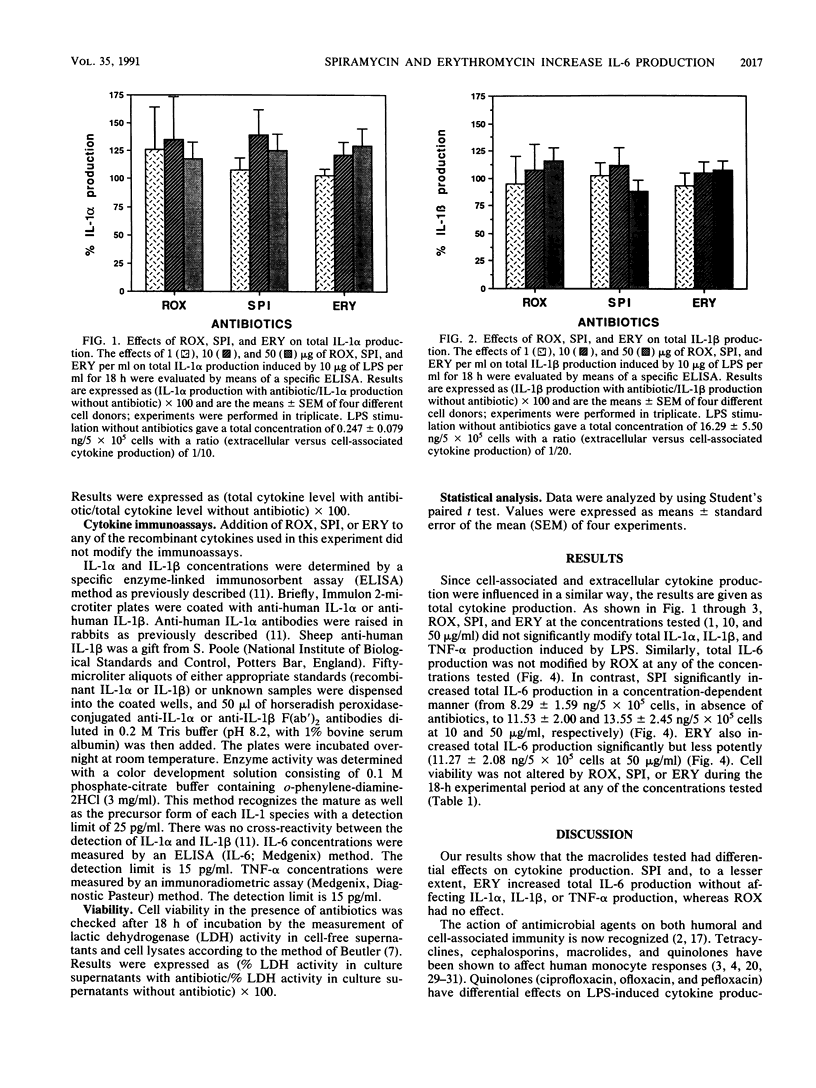
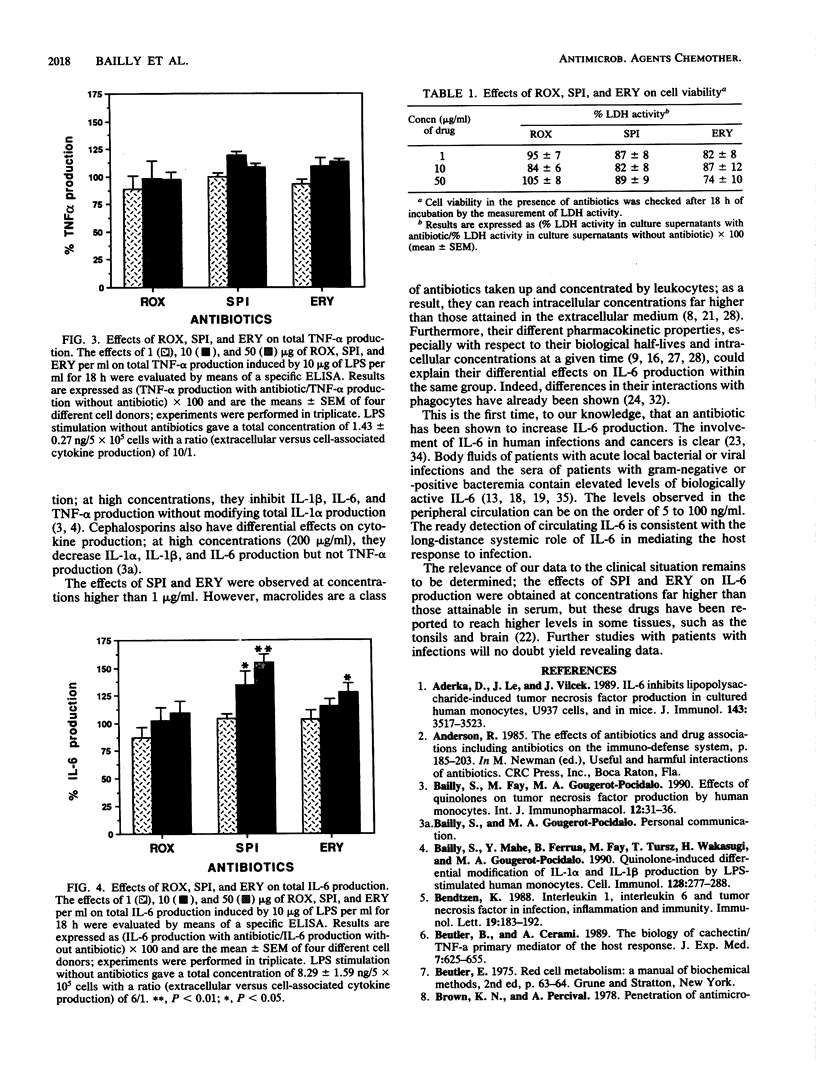
Antibiotics do not act alone but act in conjunction with the host defense system. In particular, it has been shown that some antibiotics can modify cytokine production. We compared the in vitro effects of three macrolides (roxithromycin, spiramycin, and erythromycin) actively concentrated by leukocytes on interleukin-1 alpha, (IL-1 alpha), IL-1 beta, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor alpha production by human monocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Our results show that the three macrolides tested have different effects on production of these cytokines. Spiramycin and, to a lesser extent, erythromycin increased total IL-6 production without affecting IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, or tumor necrosis factor alpha production, whereas roxithromycin had no effect. To our knowledge, this is the first time that an antibiotic has been shown to increase IL-6 production.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderka D., Le J. M., Vilcek J. IL-6 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor production in cultured human monocytes, U937 cells, and in mice. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3517–3523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly S., Fay M., Roche Y., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A. Effects of quinolones on tumor necrosis factor production by human monocytes. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1990;12(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(90)90065-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly S., Mahe Y., Ferrua B., Fay M., Tursz T., Wakasugi H., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A. Quinolone-induced differential modification of IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta production by LPS-stimulated human monocytes. Cell Immunol. 1990 Jun;128(1):277–288. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90025-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendtzen K. Interleukin 1, interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor in infection, inflammation and immunity. Immunol Lett. 1988 Nov;19(3):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(88)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Percival A. Penetration of antimicrobials into tissue culture cells and leucocytes. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):251–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. B., Zenebergh A., Tulkens P. M. Cellular uptake and subcellular distribution of roxithromycin and erythromycin in phagocytic cells. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Nov;20 (Suppl B):47–56. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.suppl_b.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and its biologically related cytokines. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:153–205. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60642-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrua B., Becker P., Schaffar L., Shaw A., Fehlmann M. Detection of human IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta at the subpicomolar level by colorimetric sandwich enzyme immunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Nov 10;114(1-2):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flad H. D., Kirchner H., Resch K. Interleukin 1 and related cytokines. Lymphokine Res. 1989 Fall;8(3):227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Moldawer L. L., Marano M., Wei H., Tatter S. B., Clarick R. H., Santhanam U., Sherris D., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Endotoxemia elicits increased circulating beta 2-IFN/IL-6 in man. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2321–2324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Banck G., Beckman H., Bellahsène A. Antibiotic-host defence interactions in vitro and in vivo. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1980;Suppl 24:195–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harf R., Panteix G., Desnottes J. F., Diallo N., Leclercq M. Spiramycin uptake by alveolar macrophages. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jul;22 (Suppl B):135–140. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_b.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser W. E., Jr, Remington J. S. Effect of antibiotics on the immune response. Am J Med. 1982 May;72(5):711–716. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90534-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfgott D. C., Tatter S. B., Santhanam U., Clarick R. H., Bhardwaj N., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Multiple forms of IFN-beta 2/IL-6 in serum and body fluids during acute bacterial infection. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):948–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssiau F. A., Bukasa K., Sindic C. J., Van Damme J., Van Snick J. Elevated levels of the 26K human hybridoma growth factor (interleukin 6) in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with acute infection of the central nervous system. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):320–323. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham E. Modulation of the proliferative response of murine thymocytes stimulated by IL-1, and enhancement of IL-1 beta secretion from mononuclear phagocytes by tetracyclines. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Jul;26(1):61–70. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Hand W. L., Francis J. B., King-Thompson N., Corwin R. W. Antibiotic uptake by alveolar macrophages. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Mar;95(3):429–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. The biology of interleukin-6. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labro M. T., el Benna J., Babin-Chevaye C. Comparison of the in-vitro effect of several macrolides on the oxidative burst of human neutrophils. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Oct;24(4):561–572. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.4.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Last-Barney K., Homon C. A., Faanes R. B., Merluzzi V. J. Synergistic and overlapping activities of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-1. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):527–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Dinarello C. A., Punsal P. I., Colten H. R. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor regulates hepatic acute-phase gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocidalo J. J., Albert F., Desnottes J. F., Kernbaum S. Intraphagocytic penetration of macrolides: in-vivo comparison of erythromycin and spiramycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jul;16 (Suppl A):167–173. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.suppl_a.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokesch R. C., Hand W. L. Antibiotic entry into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):373–380. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche Y., Fay M., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A. Effects of quinolones on interleukin 1 production in vitro by human monocytes. Immunopharmacology. 1987 Apr;13(2):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(87)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche Y., Fay M., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A. Interleukin-1 production by antibiotic-treated human monocytes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 May;21(5):597–607. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.5.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche Y., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A., Fay M., Etienne D., Forest N., Pocidalo J. J. Comparative effects of quinolones on human mononuclear leucocyte functions. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Jun;19(6):781–790. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.6.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche Y., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A., Fay M., Forest N., Pocidalo J. J. Macrolides and immunity: effects of erythromycin and spiramycin on human mononuclear cell proliferation. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Feb;17(2):195–203. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.2.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Waage A., Aarden L., Espevik T. Endotoxin, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1 induce interleukin 6 production in vivo. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Dec;53(3):488–498. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:253–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Brandtzaeg P., Halstensen A., Kierulf P., Espevik T. The complex pattern of cytokines in serum from patients with meningococcal septic shock. Association between interleukin 6, interleukin 1, and fatal outcome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


