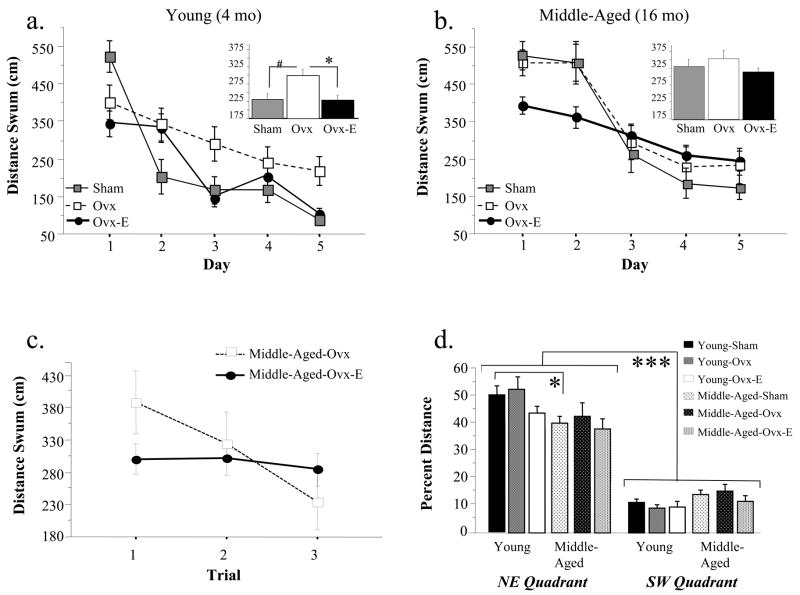
Figure 1.
For Study 1, mean± SE distance scores (cm) across days of testing on the Morris maze for (a) Young Sham, Ovx and Ovx-E groups and (b) Middle-Aged Sham, Ovx and Ovx-E groups; the inset graphs represent the data collapsed across days. For Young animals, Ovx impaired performance on the latter portion of testing, as represented by the Ovx x Day interaction. There was no effect of Ovx in middle-aged animals. Estradiol treatment enhanced performance in both age groups. Thus, there was a dissociation between sensitivity to Ovx and responsiveness to estradiol replacement. (c) Mean±SE distance scores for each trial for days 2–5 for Middle-Aged-Ovx and Middle-Aged-Ovx-E groups for Study 1. There was a significant Trial x Estradiol Treatment interaction, indicating that estradiol aided in remembering the platform location overnight in middle-aged rats. (d) Mean percent distance±SE spent in the target (NE) and opposite (SW) quadrant for each treatment group within each age for Study 1. Neither Ovx nor estradiol replacement influenced performance on the probe trial. All groups localized to the platform location, spending a greater percent distance in the target versus the opposite quadrant. * p < .05, # p = .06, *** p < .0001