Figure 1. Phosphorylation of Bim isoforms.
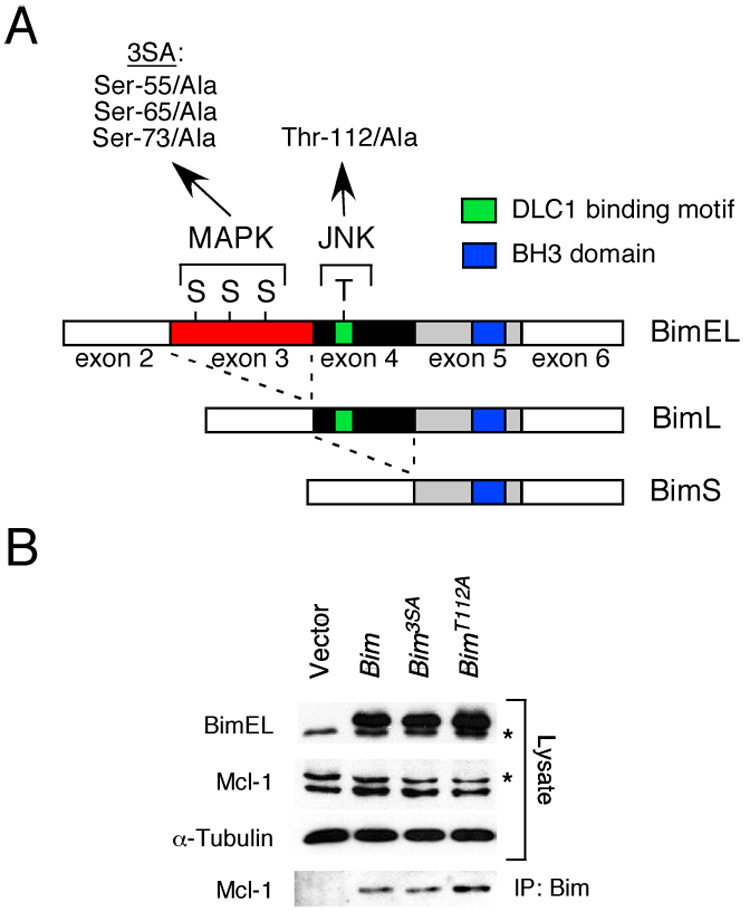
A) The structure of BimEL, which is encoded by sequences derived from exons 2–6 of the Bim gene, is illustrated schematically. Alternative splicing can delete sequences derived from exon 3 (BimL) or exons 3 & 4 (BimS) and creates two additional Bim isoforms. Three sites of MAPK phosphorylation are encoded by exon 3 (Ser-55, Ser-65, and Ser-73) and one site of JNK phosphorylation is encoded by exon 4 (Thr-112). Mutation of the three sites of Ser phosphorylation (3SA) and the site of Thr phosphorylation (Thr112A) by replacement with Ala residues is indicated. The BH3 domain and the dynein light chain 1 (DLC1) binding motif are illustrated.
B) Recombinant BimEL proteins with mutations at the three sites of MAPK phosphorylation (3SA) or the JNK phosphorylation site (Thr-112) were expressed in 293T cells. The endogenous (asterisk) and recombinant BimEL proteins were detected by immunoblot analysis. Endogenous Mcl-1 (asterisk indicates a non-specific band) and α-Tubulin were also examined. Bim/Mcl-1 complexes were examined by immunoprecipitation (IP) of recombinant Bim proteins with an antibody to the Flag epitope-tag and immunoblot analysis with an antibody to Mcl-1.
