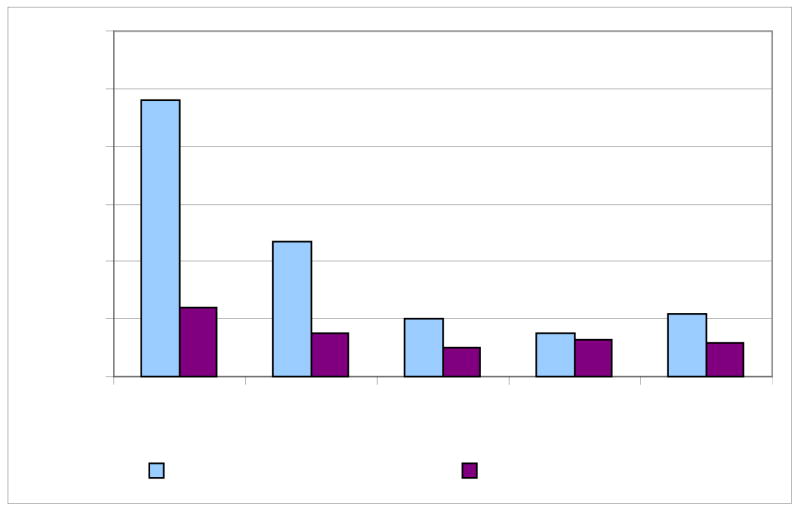
Fig 2. Neonatal respiratory morbidity after elective caesarean section and intended vaginal delivery for 34 458 pregnancies at Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark, 1998–2006. Infants with meconium aspiration syndrome, sepsis, or pneumonia excluded.
Adjusted for smoking, alcohol intake, parity, body mass index, marital status, maternal age, and years of schooling.
Adapted from Hansen AK, Wisborg K, Uldbjerg N, et al: Risk of respiratory morbidity in term infants delivered by elective caesarean section: cohort study. Bmj 336:85, 2008, with permission