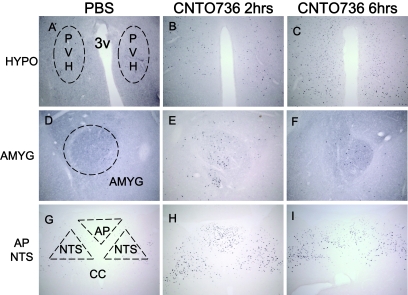
FIG. 6.
Peripheral treatment of CNTO736 leads to neuronal activation of several brain areas as measured by c-fos immunohistochemical staining. Brain sections from rats (n = 3) dosed intravenously with PBS (A, D, and G), CNTO736 for 2 h (B, E, and H), and CNTO736 for 6 h (C, F, and I). Brain sections were taken at the level of the hypothalamus (HYPO) (A–C), central nucleus of the amygdale (AMYG) (D–F), area postrema (AP), and nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) (G–I). The images are representative of sections taken from three rats per group. Coronal brain sections were stained with an anti–c-fos antibody. All pictures were taken at a ×10 magnification. Staining of PBS-treated animals at 2 and 6 h postinjection were identical. PVH, paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus.