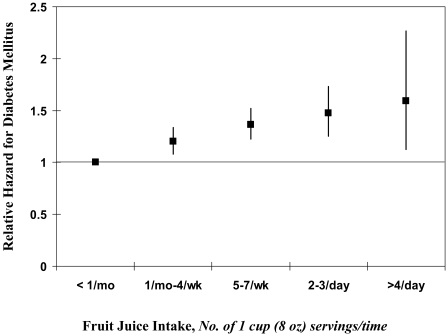
Figure 1—
Multivariate-adjusted relative hazard of diabetes by category of cumulatively updated fruit juice intake. Values were adjusted for cumulatively updated BMI, physical activity, family history of diabetes, postmenopausal hormone use, alcohol use, smoking, and total energy intake. For an increase of 1 serving/day of fruit juice, the multivariate-adjusted relative risk was 1.18 (95% CI 1.10–1.26; P < 0.0001).