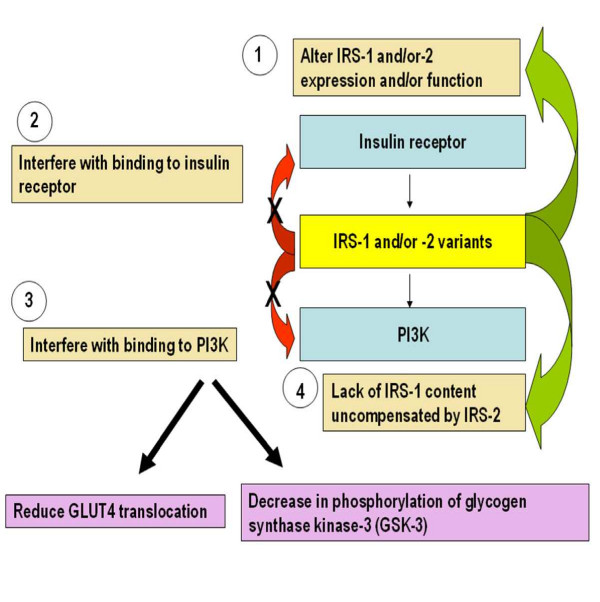
Figure 3.
Contribution of IRS-1 and/or-2 variants to Insulin Resistance. Mechanisms by which IRS-1 and/or -2 variants contribute to insulin resistance include: 1) altering IRS-1 and/or-2 expression and function, 2) reduced IRS-1 and/or -2 binding to the insulin receptor, 3) a defect in binding of IRS-1 and/or -2 variant (s) to the p85 regulatory subunit of the PI3-kinase and a decrease in PI3-kinase activity. The latter leads to either a decreased GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane, further reducing glucose transport and glycogen synthesis, or a significant IRS-1 and/or -2 -induced decrease in phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3), an enzyme that is important in glycogen synthesis, thus causing reduced glycogen synthesis, 4) reduced IRS-1 content that is not compensated by a constitutive increase in the IRS-2 protein content. This result in a reduced insulin-stimulated PI3-kinase activity and a significant decrease in Akt phosphorylation and activity.