Figure 3.
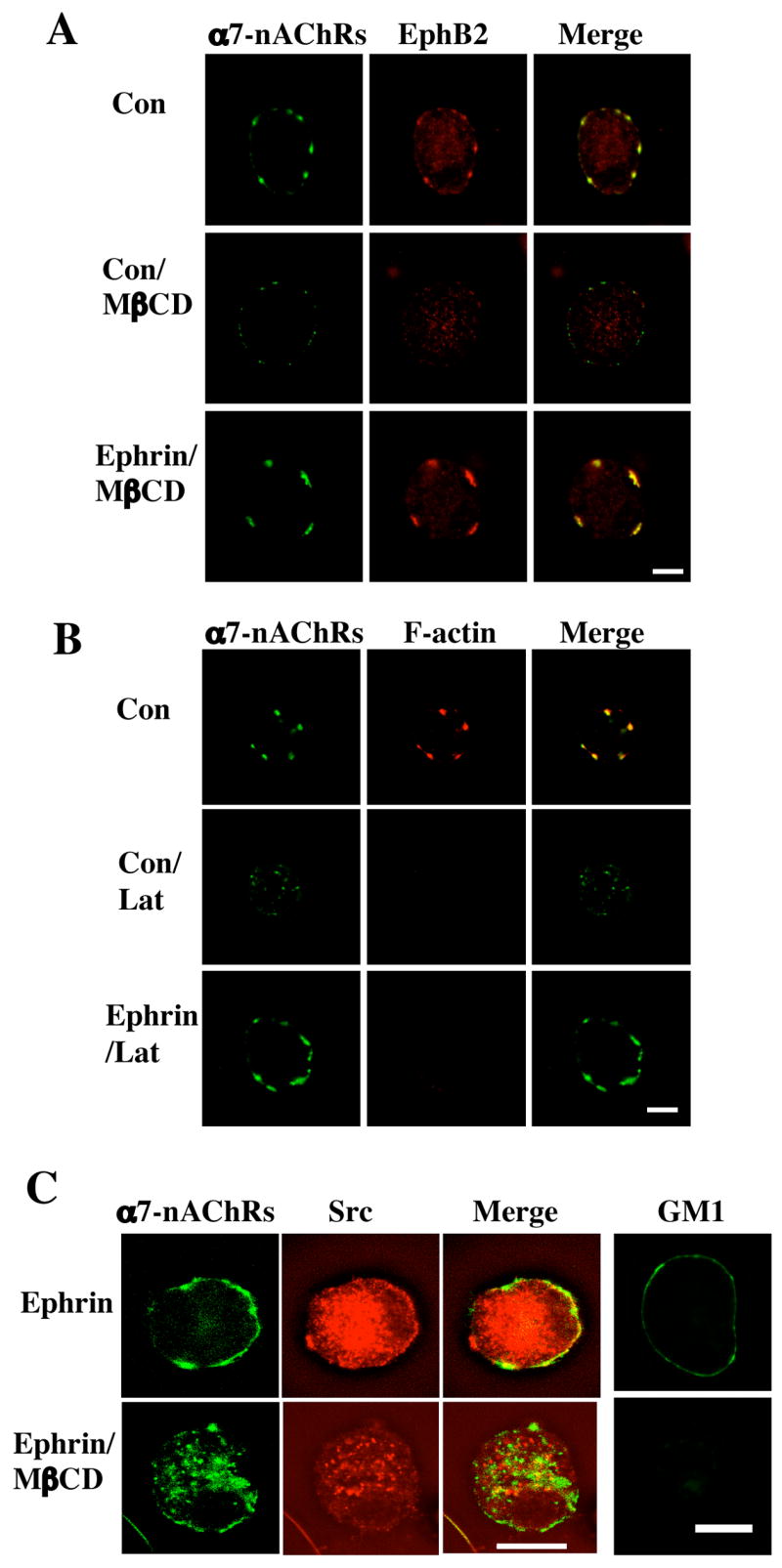
Retention of α7-nAChRs by ephrinB1/EphB2Rs after spine collapse or lipid raft dispersal. Freshly dissociated E14 CG neurons were either treated with ephrinB1-Fc/Ab to activate EphBRs (Ephrin) or with Fc/Ab as a control (Con) and then treated with methyl-βcyclodextrin (MβCD) to extract cholesterol and disperse lipid rafts or with latrunculin A (Lat) to collapse F-actin and induce spine retraction. The cells were then labeled for α7-nAChRs (left; green) and either (A) EphB2Rs, (B) F-actin, or (C) Src (middle; red), and the images merged (right; yellow). Alternatively, the cells were immunostained with cholera toxin for the ganglioside GM1, confirming that MβCD treatment dispersed the lipid rafts (C, far right). Scale bar: 10 μm. EphrinB1-Fc/Ab protected both EphB2Rs and α7-nAChRs from dispersal after spine retraction or raft disruption; it did not protect Src from dispersal.
