Figure 6.
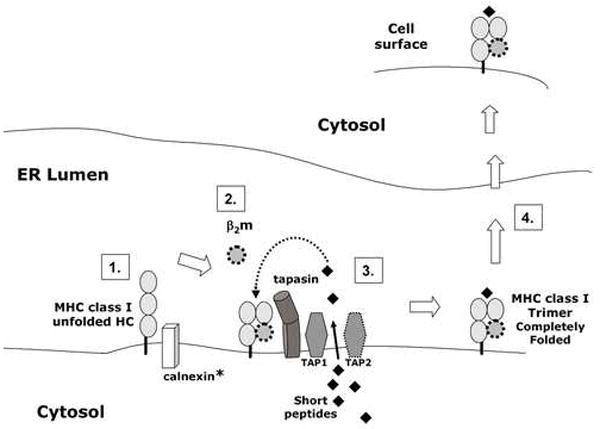
Diagram of likely pathway for MHC class Ia and class Ib cell surface expression. The illustration is based on results presented in this paper and a recent review of MHC class I antigen presentation (Cresswell et al., 2005). 1. In the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the MHC class Ia heavy chain (HC) interacts with calnexin to facilitate folding into its native conformation. *However, Qa-2 (MHC class Ib) lacks the calnexin binding site and is likely to fold in the absence of calnexin. 2. Properly folded MHC class I heavy chain noncovently binds to β2 microglobulin (β2m). 3. The TAP complex (TAP1/TAP2), tapasin, MHC heavy chain and β2m are part of the peptide loading complex. The TAP complex actively transports short peptides, produced by proteosome-mediated degradation of proteins, into the ER lumen from the cytosol. Tapasin facilitates the loading of high affinity peptide into the MHC class I peptide binding groove. 4. After the MHC class I trimer (heavy chain, β2m and peptide) is assembled, the MHC class I protein is transported to the embryo cell surface via the Golgi apparatus. ER=endoplasmic reticulum; HC= heavy chain; β2m= β2 microglobulin; TAP = transporter associated with antigen processing.
