FIGURE 3.
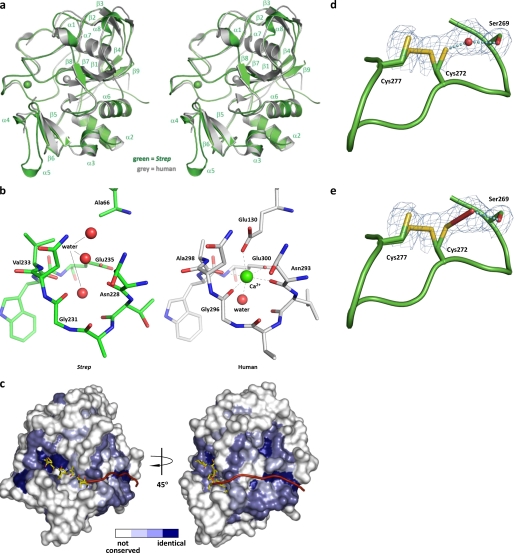
Structure of S. coelicolor FGE. a, stereo superposition of S. coelicolor FGE (green) and human FGE (gray). S. coelicolor FGE secondary structure elements are indicated. Ca2+ ions are rendered as spheres. Overall root mean square deviation is 0.65 Å. Strep, S. coelicolor. b, comparison of the residues surrounding the potential Ca2+ binding site of S. coelicolor FGE and the second Ca2+ binding site of human FGE. Proper coordination geometry is impaired with a E66A mutation in S. coelicolor FGE. Water molecules are rendered as red spheres, and Ca2+ is rendered as a green sphere. c, surface representation of the putative exosite of S. coelicolor FGE. The surface is colored according to residue conservation between all known and putative FGEs (based on amino acid sequence alignment); white represents non-conserved residues, light blue represents weakly conserved residues, medium blue represents conserved residues, and dark blue represents identical residues. The 6-residue peptide substrate is modeled from the human FGE-peptide complex structure (37) (Protein Data Bank entry 2AIK). A hypothetical extended peptide substrate is represented as a red ribbon. d and e, active site cysteines 272 and 277 appear to exist in a partial disulfide bond. Cys-272 is shown in two alternate conformations. Electron density between Cys-272 and Ser-269 has been modeled as a water molecule (d) but also is consistent with formation of a hydroperoxide at partial occupancy (e). Monomer E is shown. Prime-and-switch map is contoured at 1.5 σ.