Fig. 1.
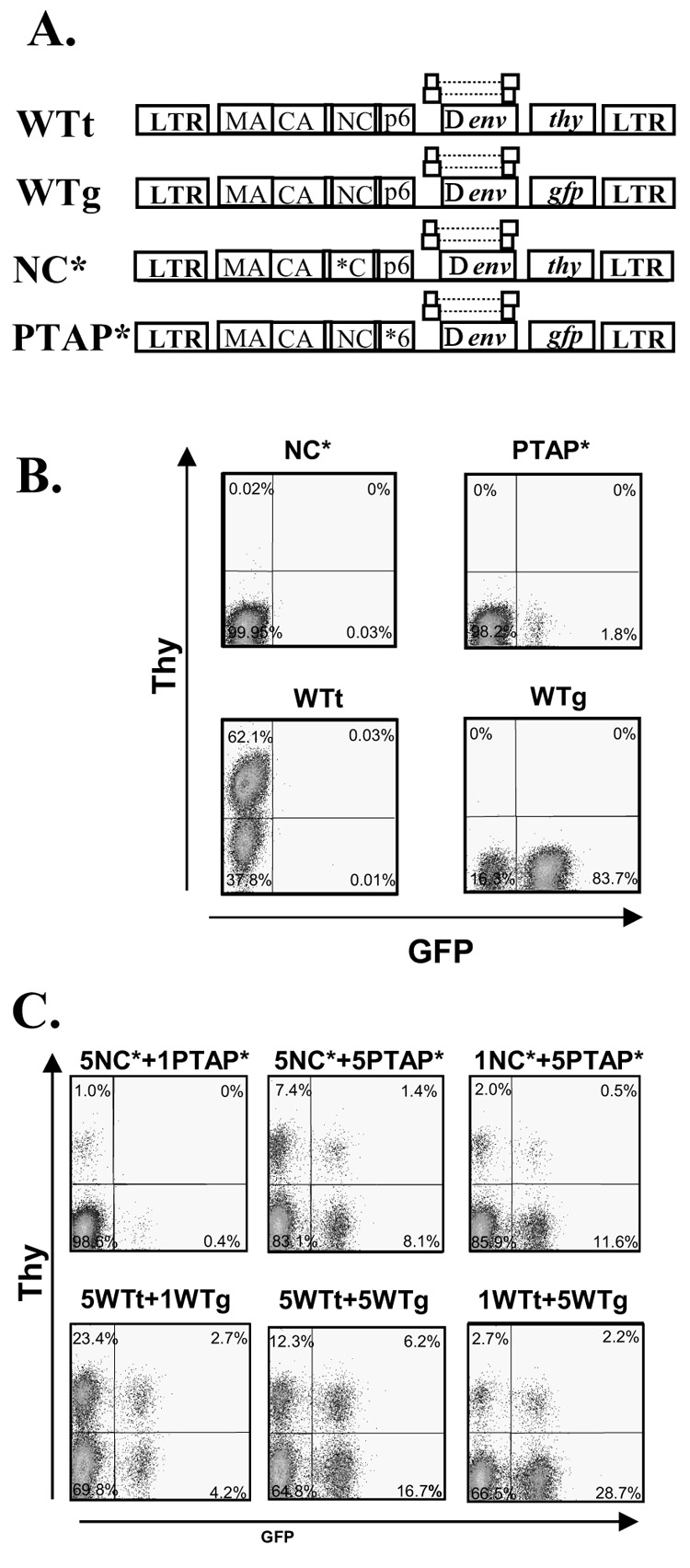
Complementation of two HIV-1 Gag mutants. (A) General structures of the HIV-1 vectors used for the complementation studies. All vectors are similar in their general structures but contain different mutations in gag (indicated by the asterisk) or marker genes. (B) Representative flow cytometry analyses of Hut78/CCR5 cells infected with wild-type or Gag mutant virus. (C) Representative flow cytometry analyses of Hut78/CCR5 cells infected with viruses generated by cotransfection of two mutants or two wild-type vectors at different ratios.
