Fig. 2. Yolk sac-derived blood cells from Brg1fl/fl:Tie2-Cre+/0 embryos undergo apoptosis at E9.5.
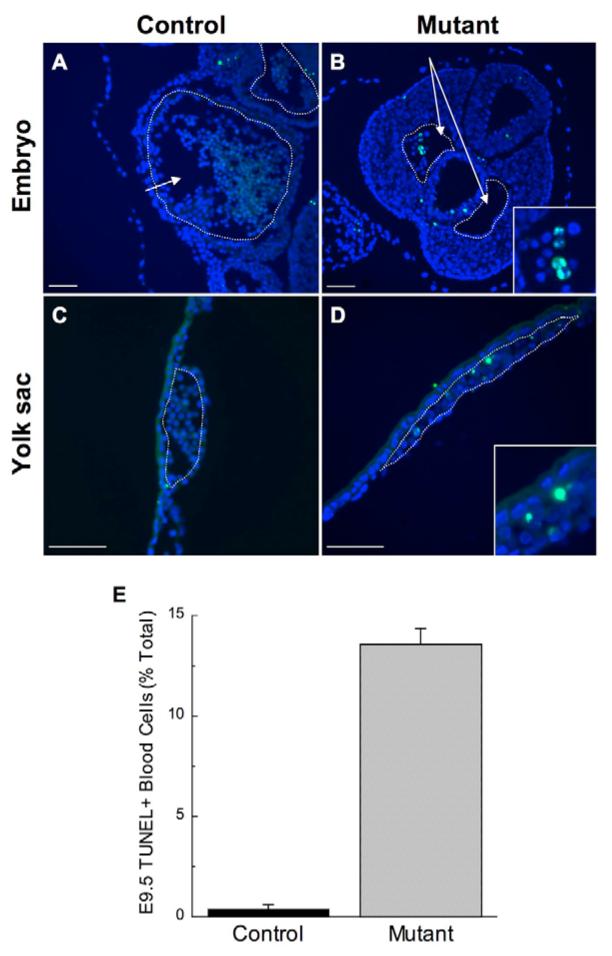
(A-D) TUNEL staining on histological sections of E9.5 littermate control Brg1fl/fl (A) and mutant Brg1fl/fl:Tie2-Cre+/0 (B) embryos, and their corresponding control (C) and mutant (D) yolk sacs. The images were merged from separate DAPI (blue) and TUNEL (green) acquisitions. The arrow in A points to the lumen of an embryonic heart (outlined in white), filled with embryonic blood cells. The inset in B focuses on TUNEL-positive blood cells found within one of the paired dorsal aortae (arrows and outlined in white) of the mutant embryo. No TUNEL-positive blood cells are detected in the control yolk sac vessel (C; outlined in white), but TUNEL-positive blood cells are evident in the mutant yolk sac vessel (D, outlined in white; shown at higher magnification in the inset in D). Scale bars: 100 μm. (E) Mean percentages of TUNEL-positive blood cells from multiple serial sections of two control and two mutant embryos stained in three independent experiments. A total of 596 and 362 blood cells were counted from control and mutant sections, respectively. Errors were calculated as s.e.m.
