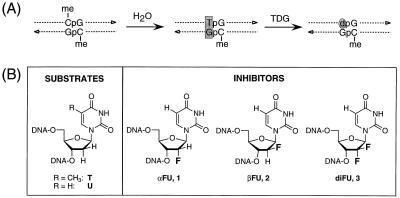
Figure 1.
(A) Deamination of m5C leads to a G/T mismatch. TDG catalyzes the glycosidic bond hydrolysis of a T residue in a G/T mismatch resulting in the formation of an AP site. TDG has a sequence preference for G/T mismatches that arise in the context of CpG sequences. (B) Substrates and inhibitors for TDG: G/T and G/U mismatches are the main substrates for TDG. Substitution of a dU residue with a dU residue containing a 2′-fluorine substituent results in a species containing a glycosidic bond with increased stability that is no longer cleavable by TDG.