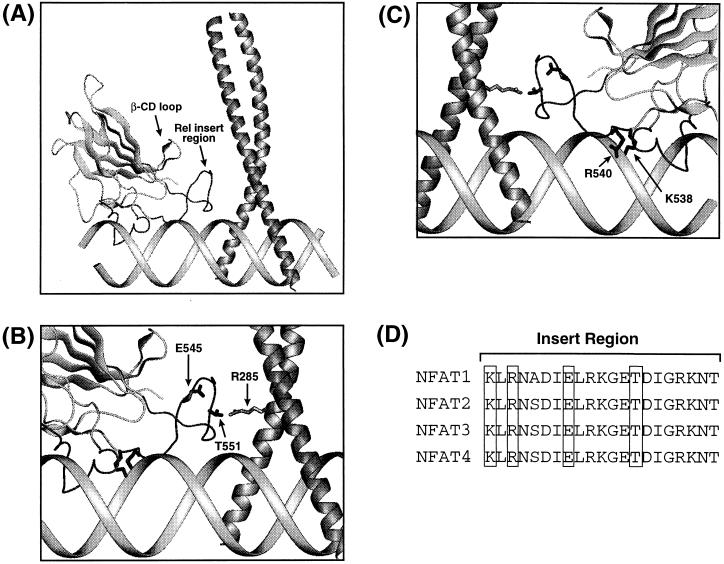
Figure 5.
(A) Model of the ternary NFAT/AP-1/DNA complex (23). The solution structure of the NFAT2-DBD (23) was superimposed with x-ray coordinates of DNA-bound p50 (30) by rigid body fitting of their respective β-barrels. The overall conformation of the NFAT RIR in the model was derived from a non DNA-bound structure and is likely to differ from that in the actual complex. The x-ray coordinates of the AP-1 bZip domain (27) were used to assemble the heterodimer over the nonconsensus AP-1 site in ARRE2, with positional and orientational information derived from affinity cleaving experiments (28). (B) An expanded view of the of the NFAT2 RIR and the junction of AP-1 between the basic and leucine-zipper domains. The side chains of three residues identified as being most critical for cooperativity (NFAT E545, NFAT T551, and c-Jun R285) are illustrated. (C) The view shown in B rotated by 180° about the vertical axis. The side chains of two NFAT residues critical for specific DNA recognition (K538 and R540) are shown. (D) Sequence alignment of the insert region of the four NFAT isoforms. Conserved residues identified here as being important for DNA recognition and cooperative binding with AP-1 are boxed.