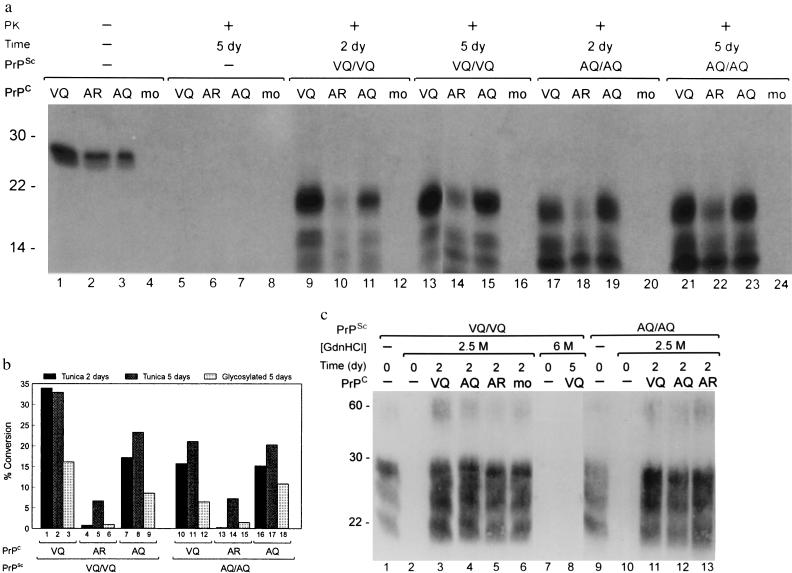
Figure 3.
(a) Cell-free conversion of nonglycosylated 35S-PrPC into protease-resistant forms. PrPSc from sheep with different PrP genotypes were pretreated in 2.5 M Gdn·HCl. The conversions were started by adding the different allelic forms of 35S-PrPC or adding controls (mo) and dilution to 1 M Gdn·HCl. Reactions were incubated for 2 or 5 days at 37°C and subsequently PK-digested (except lanes 1–4). Lanes 1–4 (starting material) contain approximately 10% of the input material for conversions shown in lanes 5–24. Samples were analyzed by 15% SDS/PAGE. Molecular mass markers (kDa) are indicated at the left. (b) Percent conversion of the different allelic forms of PrPC into PrP-res using different ShPrPSc isolates. Conversion percentages from a were determined by dividing the integrated intensities of bands at 21 kDa (lanes 5–24) by the integrated intensities of bands at 27 kDa (lanes 1–4) and multiplication by 10 (starting material = 10%). To give an indication of conversion efficiencies in conversions with glycosylated PrPC, the bands between 27–39 kDa (Fig. 2, lanes 1–3) and between 21–33 kDa (Fig. 2, lanes 10–15) were also quantified. The different types of conversions using either nonglycosylated PrPC or glycosylated PrPC, as well as the length of the incubation time in days (dy) and the allelic forms of PrPSc and PrPC, are indicated. (c) Immunoblot analysis using the R521–7 antibody after PK digestion of 1/10 vol of the conversion reactions shown in a. Indicated are the different allelic forms of PrPSc and PrPC, the renaturation time, and the concentration (M) of Gdn·HCl used to pretreat the PrPSc. Untreated PrPSc (starting material) is shown in lanes 1 and 9. Molecular mass markers (kDa) are indicated at the left.