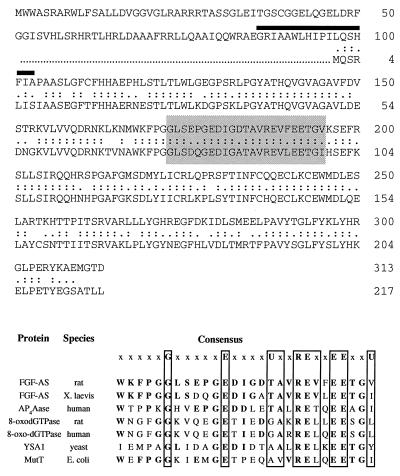
Figure 5.
(Upper) Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequence of rat and Xenopus FGF-2 antisense cDNA clones. Double and single dots represent amino acid identity and similarity, respectively. Percentages of identity and similarity between rat and Xenopus antisense amino acid sequences are 69% and 89%, respectively. The location of a putative transmembrane domain (amino acids 89–107) is indicated by a heavy overline. The conserved MutT domain is shaded. (Lower) Comparison of the MutT domain and flanking sequence of the FGF-AS protein with those of other members of the MutT/Nudix family of proteins. In the consensus sequence (top line) U represents a bulky aliphatic amino acid (I, L, or V) and x may be any amino acid. Bold letters indicate identities with the rat FGF-AS protein sequence. The indicated sequences are P13420P13420 (Xenopus FGF-AS); U30313U30313 (human Ap4Aase); D49977D49977 and P36639P36639 (rat and human 8-oxo-dGTPase); Q01976Q01976 (yeast YSA1); and P08377P08377 (Escherichia coli MutT).