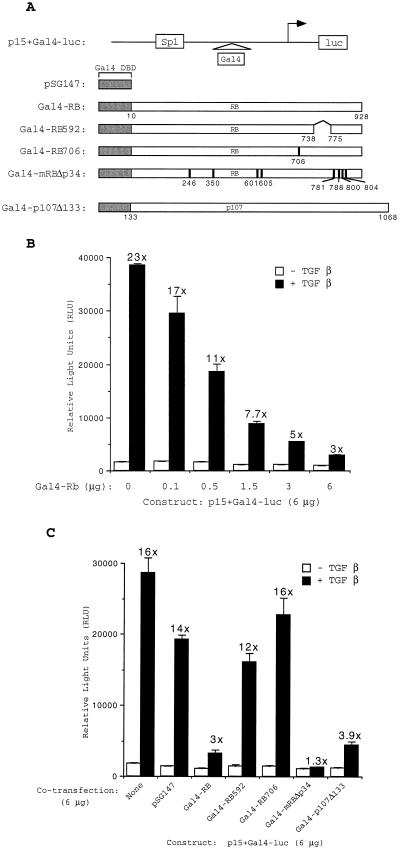
Figure 5.
Promoter-bound RB and p107 suppress TGF-β-mediated gene expression from p15INK4B promoter. (A) Gal4 DNA binding sites were introduced into the p15-luc construct to obtain p15+Gal4-luc. Various Gal4 fusion constructs are shown. pSG147, vector plasmid containing the amino acids 1–147 of the yeast Gal4 DNA binding domain (Gal4 DBD); Gal4-RB, fusion protein construct between the Gal4 DNA binding domain and the human RB missing the first 10 amino acids; Gal4-RB592, same as Gal4-RB but containing deletions from amino acids 738–775; Gal4-RB706, same as Gal4-RB but with a point mutation at amino acid 706; Gal4-mRBΔp34, fusion protein construct between the Gal4 DNA binding domain and the mouse RB homologue, which has all eight potential phosphorylation sites (at amino acids 246, 350, 601, 605, 781, 788, 800, and 804) mutated; Gal4-p107Δ133, fusion protein construct between the Gal4 DNA binding domain and the human p107 from amino acids 133–1,068. Solid vertical bars denote specific amino acid mutations. (B) p15+Gal4-luc construct was cotransfected with increasing amounts of Gal4-RB DNA, as indicated, into HaCaT cells, and their luciferase activity was assayed as described for Fig. 3B. Induction folds by TGF-β are indicated. Error bars = SD of duplicates. (C) p15+Gal4-luc construct was cotransfected with different Gal4 fusion constructs, as indicated, and luciferase activities were assayed as described for Fig. 3B. Induction folds by TGF-β are indicated. Error bars = SD of duplicates.