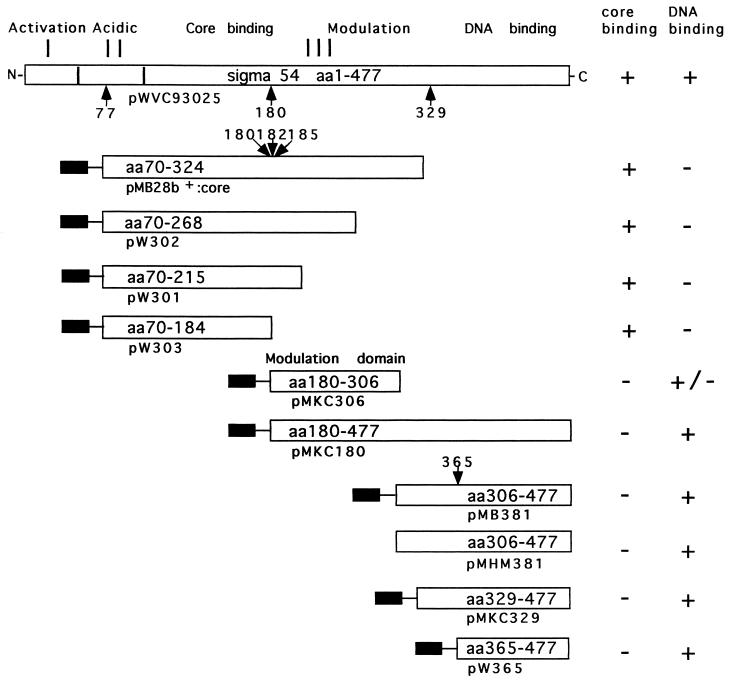
Figure 1.
The primary organization of σN and its functional domains (8, 14, 15). Amino acids 1–477 of the K. pneumoniae protein can be divided into regions I–III (13). Region I is glutamine-rich and involved in activation of the holoenzyme (28–30), region II is acidic and is variable among members of the σN protein family (8, 23) and region III includes the core binding determinant, the DNA-binding domain, and the domain described in this paper which enhances and modulates DNA-binding activity (8, 14, 15, 18). Arrows mark proteolytically sensitive sites (21) relevant to this work, and the amino acid residue C terminal to the cleavage site is indicated. The site at 365 was established by chymotryptic challenge of purified peptides comprising amino acids 329–477 and 306–477 and searching for common peptides and the site at 185 by tryptic challenge of the 70–324 peptide (X.-Y.W. and M.B., unpublished data); the other sites have been previously reported (15, 21). Protein fragments employed in this work are shown and their activities are indicated. Plasmids directing peptide synthesis are indicated below each protein fragment, and the solid bar the N-terminal extension-MGSSH6SSGLVPRGSHM arising from the vector. In the case of the 365–477 and 306–477 peptides the Met at 365 and at 306 is contributed by this extension. The activity that enhances DNA-binding resides in peptide 180–306 approximates a 180–303 chymotryptic peptide of σN (15, 21).