Fig. 1.
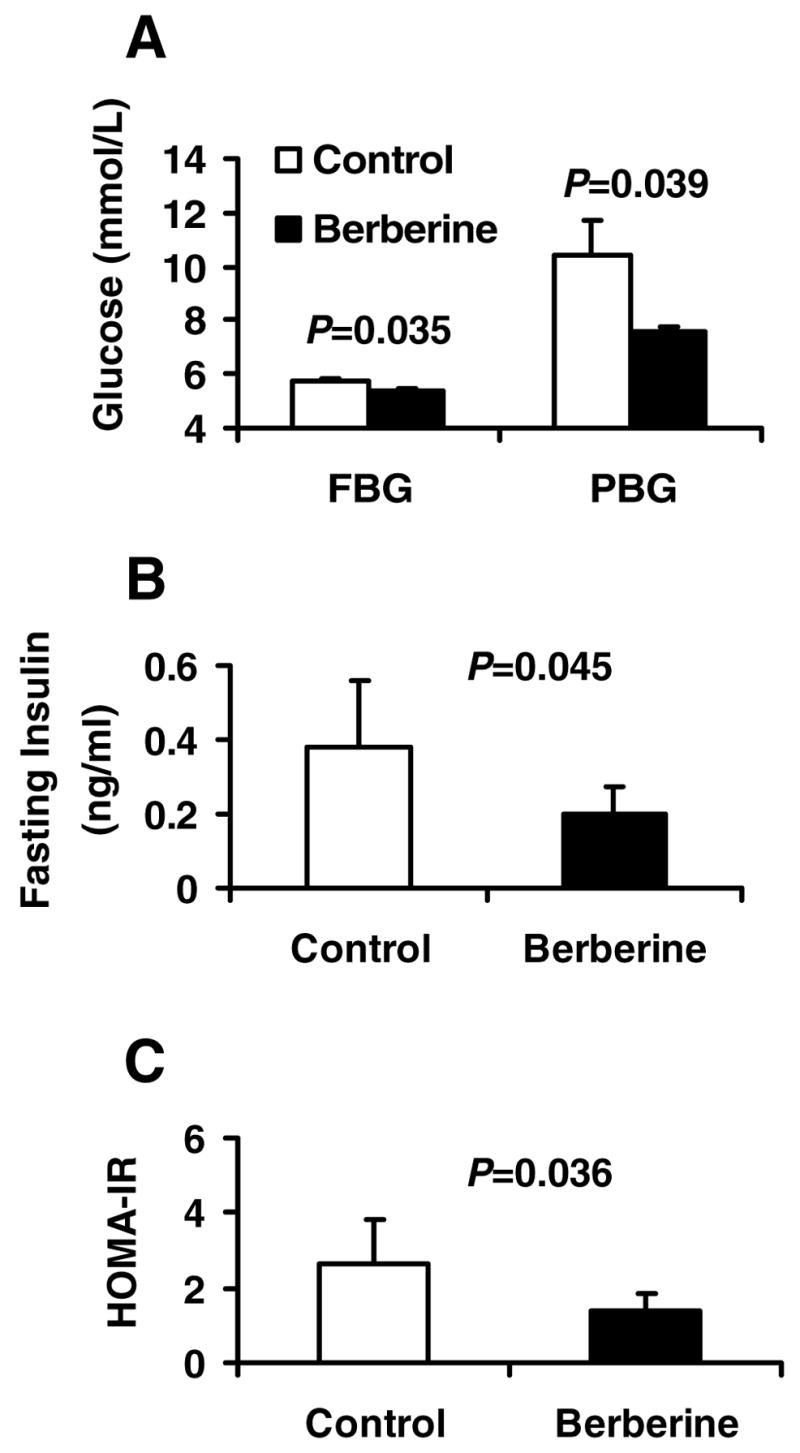
Berberine improved glucose metabolism in dietary obese rats. Twelve HFD fed rats were divided into control (n=6) and berberine-treated (n=6) groups. The treated rats were given berberine at 125 mg/Kg body weight twice a day by gastric gavage for 5 weeks. The control rats were gavaged with an equal volume of vehicle (distilled water). After 5-week treatment, intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT) was conducted after 10 hours fasting. A: Fasting blood glucose (FBG) and 2 hour postprandial blood glucose (PBG) determined during IPGTT in the rats. B: Fasting serum insulin levels in control and berberine-treated rats. C: HOMA-IR calculated by fasting serum insulin and FBG of the control and berberine treated rats.
