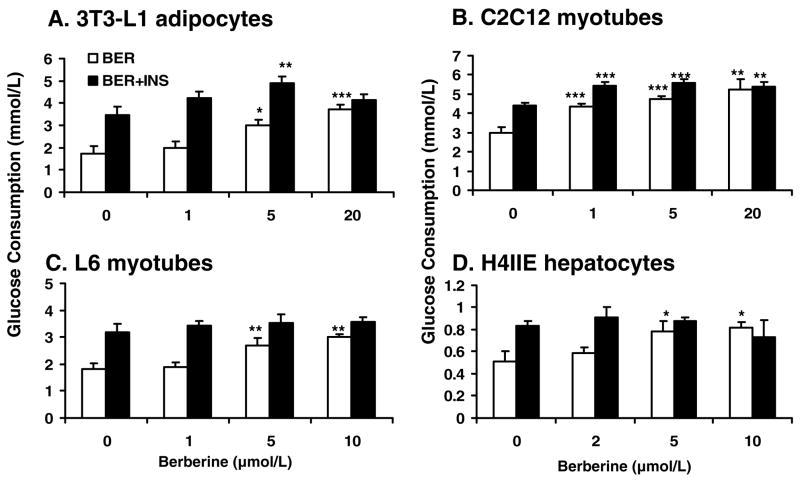
Fig. 2.
Berberine (BER) increased glucose consumption in a dose-dependent manner. The cells were cultured in a 96-well plate. When experiments, the normal culture medium was replaced by serum-free DMEM supplemented with bovine serum albumin at 0.25%. Then, the cells were treated with berberine for 24 hours. Insulin was used in the positive control (INS; final concentration 100 nmol/L). A: Glucose consumption in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. B: Glucose consumption in C2C12 myotubes. C: Glucose consumption in L6 myotubes. D: Glucose consumption in H4IIE hepatocytes. Data was expressed as means ± SEM (n=8). Compared with control (0 μmol/L): *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001