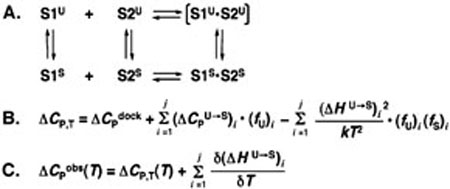FIGURE 1.
Coupling of single strand stacking equilibria to nucleic acid duplex formation. (A) Schematic depicting the formation of duplex from component strands S1 and S2. Each strand participates in an equilibrium between unstacked (U) and stacked (S) states. Strand stacking is coupled to duplex formation, so duplex composed of unstacked strands is bracketed to indicate that it is a virtual state. (B) Equation showing the components of ΔCp observed for duplex formation at a given temperature. ΔCpdock refers to the intrinsic ΔCp for helix formation from stacked strands; the second term refers to the intrinsic ΔCp for conversion of single strands from unstacked to stacked states weighted by the fraction of unstacked strands. Here, ΔCpU→S is summed over contributions from both S1 and S2; the third term refers to the contribution to ΔCp arising from the linkage of fluctuating intermediates that shift in fractional population as a function of duplex formation and is also summed over contributions from both strands. (C) Equation showing the dependence of the observed ΔCp on temperature in the case of coupling to temperature-dependent equilibria. In addition to the phenomena shown in (B), fractional unfolding of single strands results in further temperature dependence of measured ΔHs that contribute to the observed ΔCp.