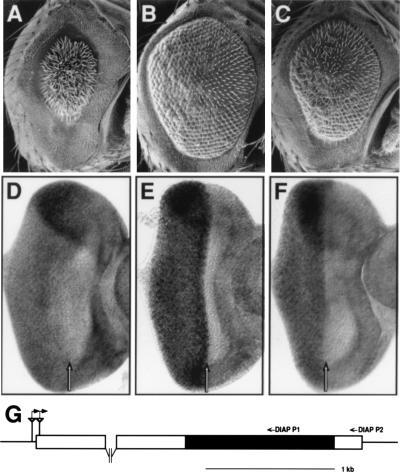
Figure 4.
GMR insertions near the DIAP1 gene act as strong suppressors of a GMR-rpr-dependent small eye phenotype and express high levels of the DIAP1 gene in the developing eye. The following genotypes are shown: GMR-rprS/TM6B (A); GMR-rprS/GMR228 (B); GMR-rprS/GMR355 (C); wild type (D); GMR228/TM6B (E); GMR355/TM6B (F). GMR-rpr expression results in a cell death-dependent small eye phenotype (A), which is suppressed in the presence of the GMR228 (B) and GMR355 (C) chromosomes. DIAP1 transcript levels are uniform throughout the wild-type eye-imaginal disc (D) but are elevated posterior to the morphogenetic furrow in the GMR228 (E) and GMR355 (F) lines. (G) Diagram of the DIAP1 chromosomal region. The P element in the GMR228 line is inserted after base 34 in the DIAP1 5′ untranslated region and 70 bases upstream of the DIAP1 5′ untranslated region in the GMR228 line. Both P elements (triangles) are oriented with the 3′ P end nearest the DIAP1 gene. The direction of hsp70 transcription is indicated by the raised, rightward pointing arrows. Small arrows above the map indicate the primers used to prime cDNA synthesis (DIAP P2) and to carry out PCR (DIAP P1) to detect the presence of chimeric DIAP1 transcripts.