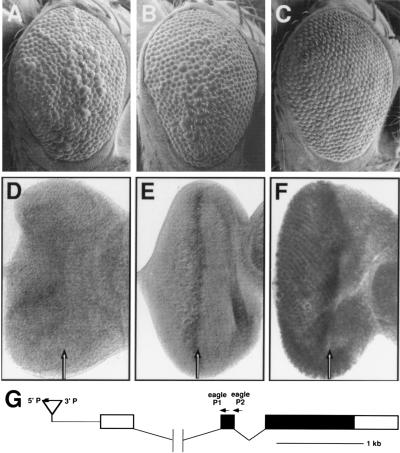
Figure 5.
A GMRE insertion near the eagle gene acts as a suppressor of the sev-Ras1V12-dependent rough eye phenotype by directing eagle expression in the developing eye. The following genotypes are shown: sev-Ras1V12 (CR2)/+ (A); sev-Ras1V12 (CR2)/GMRE28 (B); sev-Ras1V12 (CR2)/GMR-eagle (C); wild type (D); GMRE28/+ (E); GMR-eagle/+ (F). Expression of sev-Ras1V12 (CR2) results in a rough eye phenotype (A). This phenotype is mildly suppressed in the presence of the GMRE28 chromosome (B) and more strongly suppressed by GMR-eagle expression (C). The degree of sev-Ras1V12 rough eye suppression is correlated with the level of eagle expression: wild-type eye imaginal discs express little if any eagle (D) discs from GMRE28 flies express eagle at higher levels in the morphogenetic furrow (arrow), and to some extent posterior to the morphogenetic furrow (E); and discs from GMR-eagle flies express high levels of eagle in and posterior to the morphogenetic furrow (F). (G) Map of the eagle genomic region. GMRE28 is inserted approximately 500 bases 5′ to the eagle transcription unit as indicated. Noncoding cDNA sequences are indicated by open boxes and coding sequences by filled boxes.