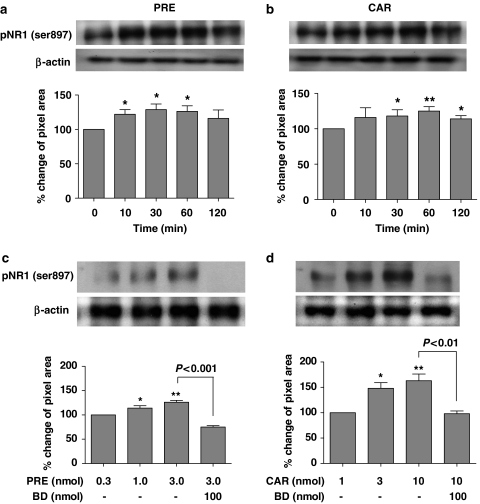
Figure 3.
Western blots and graphs illustrating the effect of i.t. treatment with Sig-1 R agonists, PRE-084 (PRE, a and c) or carbetapentane (CAR, b and d) on PKA-dependent pNR1 (122 kDa) in the spinal dorsal horn. Expression of pNR1 (Ser897) in the spinal cord dorsal horn was found to increase as early as 10 min after i.t. injection of either PRE-084(3 nmol, a) or carbetapentane (10 nmol, b), and peaked between 30–60 min post-injection. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 as compared with those of non-treated mice; indicated by the ‘0' time point in panels (a) and (b). Protein expression of pNR1 before treatment with Sig-1 R agonists was calculated as 100%. I.t. injection of PRE-084 (0.3, 1 and 3 nmol, c) or carbetapentane (1, 3 and 10 nmol, d) dose dependently increased the expression of the pNR1 (Ser897) subunit in the spinal cord dorsal horn. I.t. pretreatment with 100 nmol BD-1047 (BD, a selective Sig-1 R antagonist) significantly reduced the increase in pNR1 (Ser897) expression induced by i.t. injection of PRE-084or CAR. Protein expression of pNR1 in response to the lowest dose of Sig-1 R agonists was calculated as 100%. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 as compared with pNR1 (Ser897) expression in response to the lowest dose of PRE-084(0.3 nmol) or carbetapentane (3 nmol). All immunoblots were normalized for analysis using β-actin (as a loading control) in each group (see text). The number of mice was five in each group. I.t., intrathecal; PKA, protein kinase A; pNR1, phosphorylation of the NMDA receptor subunit NR1; Sig-1 R, sigma-1 receptor.