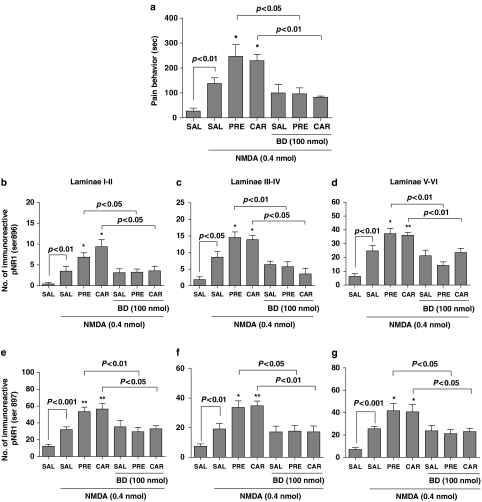
Figure 6.
Effect of i.t. treatment with PRE-084 (PRE) or carbetapentane (CAR) on NMDA-induced pain-associated behaviors and NMDA-induced PKC and PKA-dependent spinal pNR1. I.t. treatment with NMDA (0.4 nmol) elicited significant nociceptive behaviors, which included caudally directed licking, scratching and biting (a), as well as a significant increase in the numbers of immunoreactive phosphorylated NR1 subunits in laminae I–II (b and e), III–IV (c and f) and V–VI (d and g) of the dorsal horn. (b–d) Sig-1 R agonist-induced PKC-dependent pNR1 (Ser896). (e–g) Sig-1 R agonist-induced PKA-dependent pNR1 (Ser897), respectively. I.t. pretreatment with PRE-084(3 nmol) or carbetapentane (10 nmol) potently enhanced i.t. NMDA-induced pain behaviors and pNR1 expression, and this enhancement was blocked by BD-1047 (BD, a selective Sig-1 R antagonist, 100 nmol) administration. Mice in the control group received i.t. saline treatment (SAL). *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 as compared with those of SAL-NMDA-treated mice. The number of mice was seven in each group. I.t., intrathecal; PKA, protein kinase A; PKC, protein kinase C; pNR1, phosphorylation of the NMDA receptor subunit NR1.