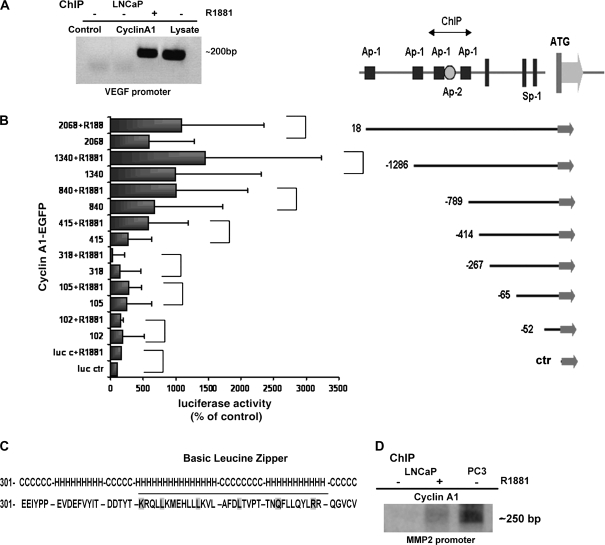
Figure 6.
Evaluation of the role of cyclin A1 in mediating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) transcriptional activity. A) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChiP) in LNCaP cells or in LNCaP cells treated with 0.1 nM R1881, a synthetic androgen. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed on immunocomplexes obtained by precipitation with antibody to cyclin A1 or to IgG (Control); Lysate = total lysate. B) The schematic organization of the VEGF promoter (25). Consensus sites for Ap-1 (filled black squares) and Ap-2 (open circle) along with translation start site and Sp-1 sites are indicated. Luciferase assay was performed in LNCaP cells that were cotransfected with pCMS-EGFP-A1 and various VEGF promoter fragments and treated with R1881 or vehicle for 24 hours. (The P values for each comparison to examine the effect of cyclin A1 overexpression on VEGF promoters were: promoter fragment 102: P = .395; 105: P = .354; 318: P = .780; 415: P = .132; 840: P = .078; 1340: P = .026, full-length promoter: P = .016; two-sided t test.) (The P values for each comparison to examine the effect of cyclin A1 overexpression in combination with R1881 were: promoter fragments 102: P = .495; 105: P = .028; 318: P = .005; 415: P = .076; 840: P = .01; 1340: P = .019; full-length promoter: P = .016; two-sided t test.) C) Secondary structure of cyclin A1 that forms the leucine-like zipper fragment. The helix-coiled-helix loop is underlined (H = helix; C = coil). D) ChiP assay in LNCaP cells or in LNCaP cells treated with 0.1 nM R1881 (+) and in PC3 cells. PCR was performed with cyclin A1 immunocomplexes as template; primers spanning the Ap-1 site as described in “Materials and Methods” in the metalloproteinase 2 promoter were used to amplify precipitated sequences.