Fig. 3.
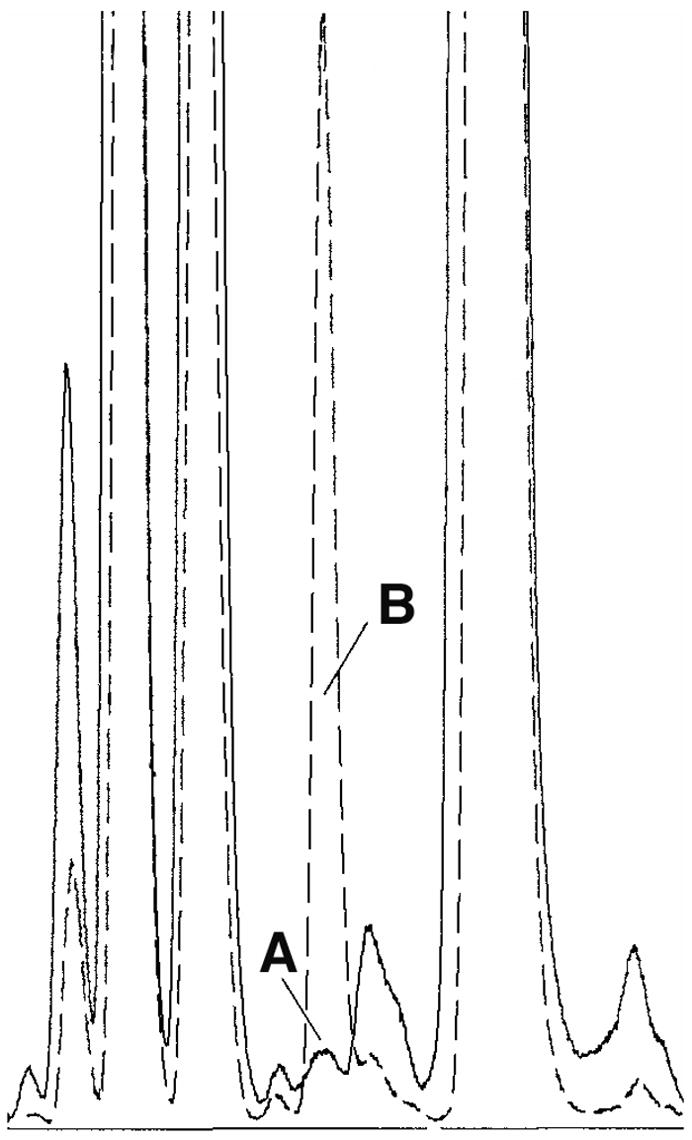
Identification within Echinacea purpurea root of 2,3-dihydroxypropyl cysteine, a structural component unique to prokaryotic lipoproteins. Lipoproteins were extracted using 4% SDS, were partitioned into phenol and then treated with proteinase K to remove the bulk of the protein component. Lipopeptide moieties were eluted from a C18 column using a water/isopropanol gradient and active fractions pooled. Active sample and the synthetic lipoprotein Pam3CSK4 (used as a standard) were hydrolyzed using methanesulfonic acid and hydrolysates analyzed using a Hewlet Packard AminoQuant System. Chromatogram section shown represents separation of active Echinacea sample (solid line) and active Echinacea sample spiked with standard (dashed line) using RP-HPLC with fluorescence detection after being derivitized with o-phthalaldehyde . Peak A eluted with a retention time (7.13 min) identical to the standard and identification was further supported by spiking of the active fraction with the standard (Peak B).
