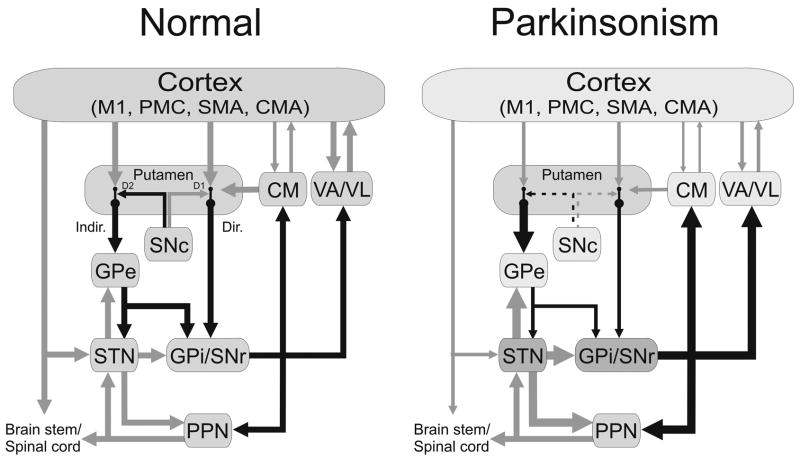
Figure 1.
Parkinsonism-related changes in overall activity (‘rate model’) in the basal ganglia-thalamocortical motor circuit. Black arrows indicate inhibitory connections; gray arrows indicate excitatory connections. The thickness of the arrows corresponds to their presumed activity. Abbreviations: CM, centromedian nucleus of thalamus; CMA, cingulate motor area; Dir., direct pathway; D1, D2, dopamine receptor subtypes; GPe, external segment of the globus pallidus; GPi, internal segment of the globus pallidus; Indir., indirect pathway; M1, primary motor cortex; Pf, parafascicular nucleus of the thalamus; PMC, premotor cortex; PPN, pedunculopontine nucleus; SMA, supplementary motor area; SNc, substantia nigra pars compacta; SNr, substantia nigra pars reticulata; STN, subthalamic nucleus; VA, ventral anterior nucleus of thalamus; VL, ventrolateral nucleus of thalamus.