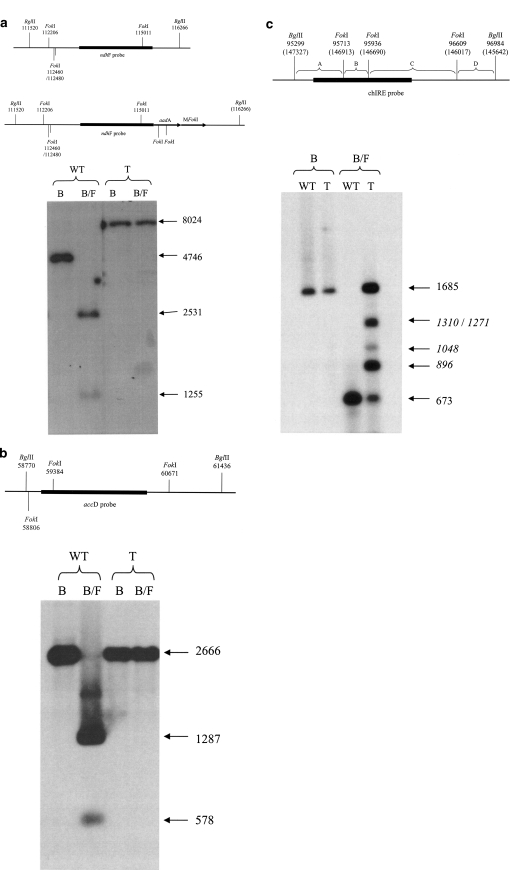
Fig. 2.
Southern analysis indicates that FokI sites are protected from digestion to varying degrees in transplastomic plants. a Digestion with BglII gives ndhF hybridizing fragments of 4,746 bp and 8,024 bp for the wild type (WT) and transplastomic (T) plants respectively. Digestion with both BglII and FokI gives bands of 2,531 and 1,255 bp for wild type but protection of all six FokI sites in the transplastomic plant means that the 8,024 bp fragment is not digested further. b FokI sites within the LSC were assayed using the accD probe indicated. In both wild type and transplastomic plants, digestion with BglII gives a fragment of 2,666 bp. Digestion with both BglII and FokI, gives the two predicted bands of 1,287 and 578 bp for wild type, but protection of the two FokI sites leaves the 2,666 bp fragment unaltered in the transplastomic plant. c FokI sites within the IR were tested using the chIRE probe indicated. Digestion of both wild type and transplastomic cpDNA with BglII gives a single band of 1,685 bp. Digestion of wild type with both BglII and FokI gives a band of 673 (the smaller 414 bp and 223 bp fragments have been run out of the gel). Digestion of transplastomic DNA with both enzymes gives bands of 1,685 (no FokI digestion) and 673 bp (full digestion). A number of additional partial digestion products are evident and their derivation can be explained as follows; 1,310 bp (A + B + C), 1,271 bp (B + C + D), 1,048 bp (C + D), 896 bp (B + C) B BglII, F FokI, WT wild type, T transplastomic