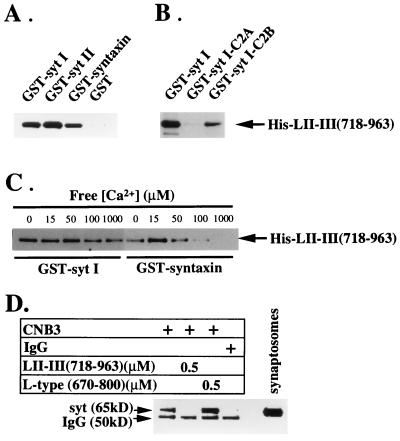
Figure 1.
Binding of the N-type Ca2+ channel synprint peptide to the C2B domain of synaptotagmin. (A) Binding of the synprint peptide [LII–III(718–963)] to GST-fusion proteins containing the full-length cytoplasmic domains of syt I and syt II, full-length syntaxin 1A, and GST alone. (B) Synprint peptide binding to the C2B domain but not the C2A domain of syt I. (C) Ca2+ independence of the interaction between the synprint peptide and syt I. GST-fusion proteins (2 μg) were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose and incubated with His-LII–III(718–963) (31 nM). The binding reactions were performed in a Ca2+ buffering system (5 mM N-hydroxyethylethylenediaminetriacetic acid-Ca2+/50 mM Hepes, pH 7.2/150 mM NaCl) containing free Ca2+ concentrations estimated using the max chelator software (version 6.63) as described. The concentrations of free Ca2+ in the binding buffers were 15 μM in A and B, and 0, 10, 20, 50, 100 μM, and 1 mM, as indicated, in C. After extensive washing with the incubation buffers, the proteins bound to the beads were eluted with 15 mM reduced glutathione in 50 mM Tris⋅HCl (pH 8), and subjected to electrophoresis and immunoblotting. The bound His-LII-III(718–963) was detected using the T7.Tag antibody. (D) N-type Ca2+ channels were solubilized from synaptosomal membranes and immunoprecipitated with the anti-CNB3 antibody (24) as described in Experimental Procedures with the additions indicated. The immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotted with antibody 1D12 against synaptotagmin. The label IgG indicates the position of the heavy chain of IgG that is labeled by the secondary antibody reagent used in the immunoblot.