Abstract
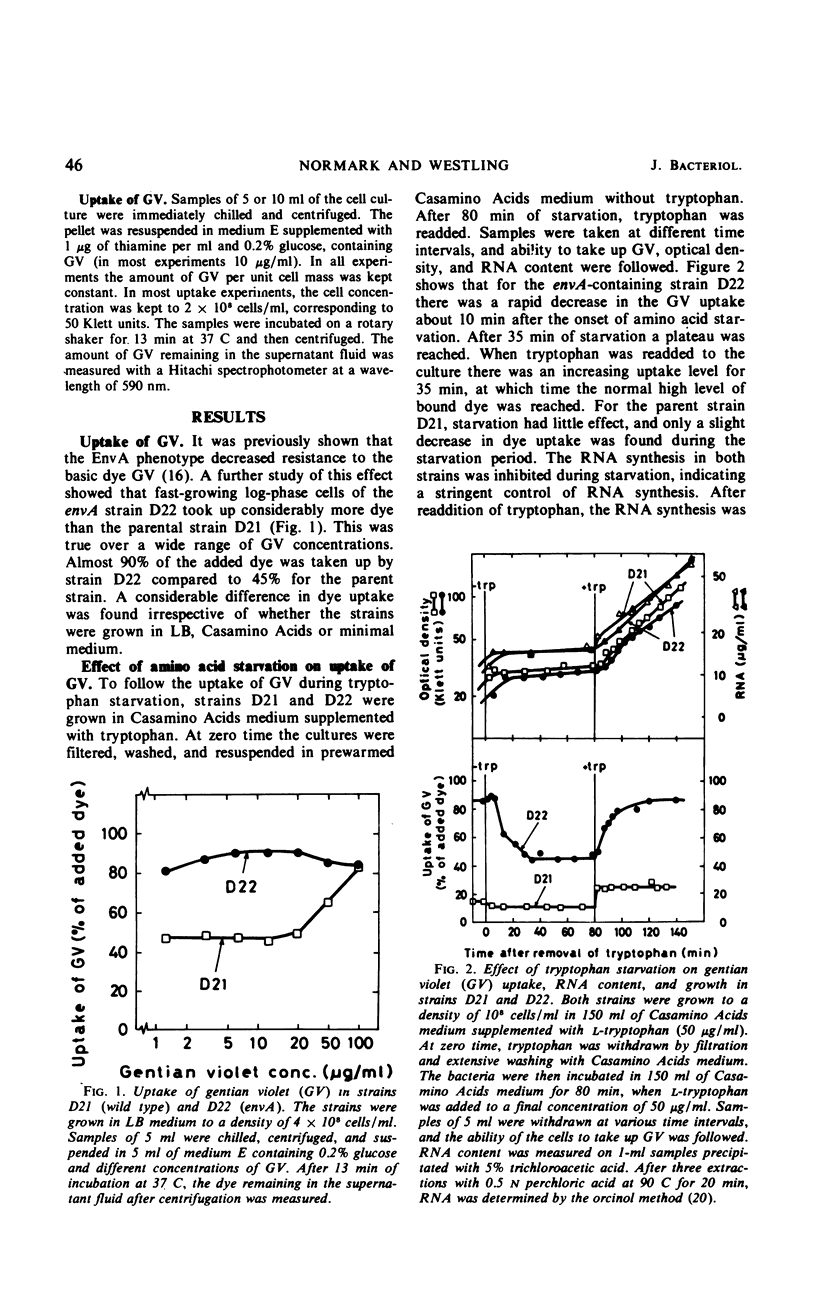
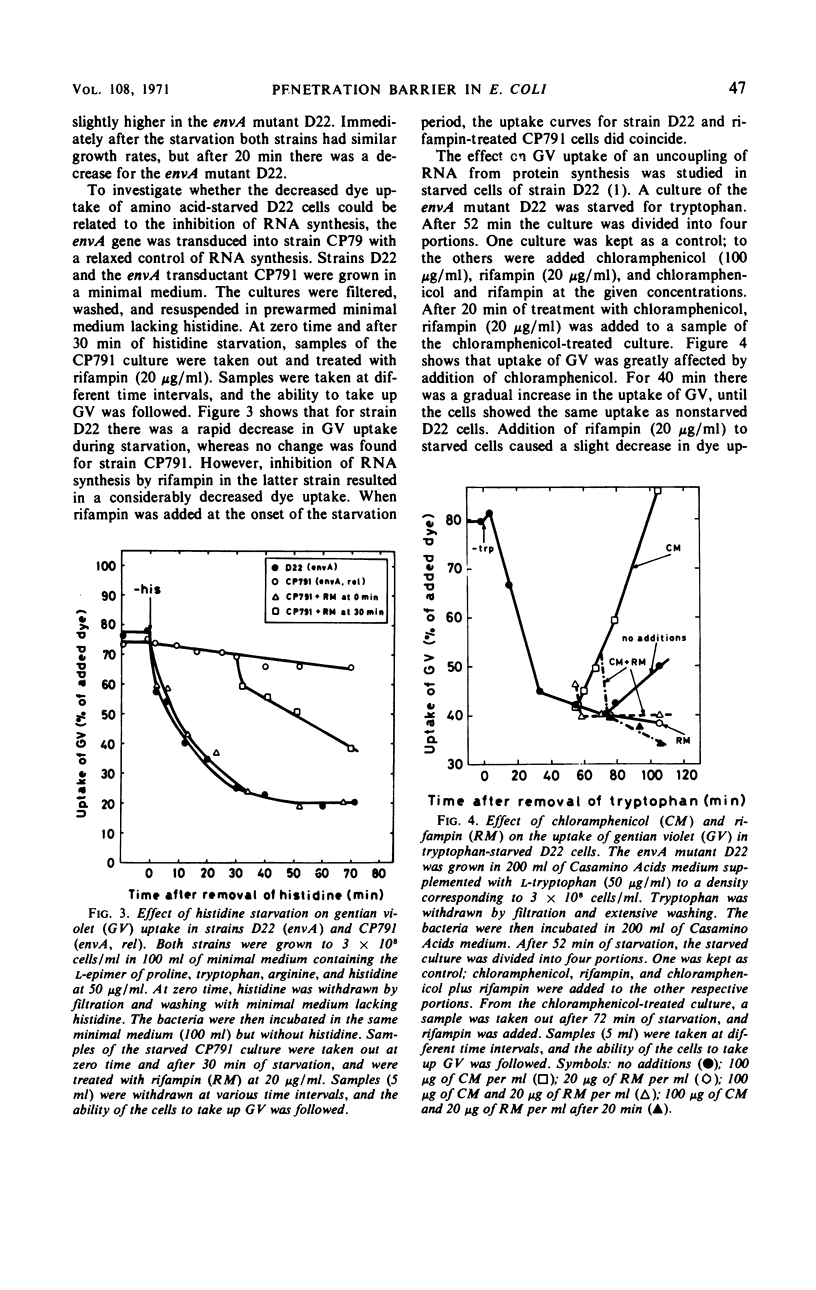
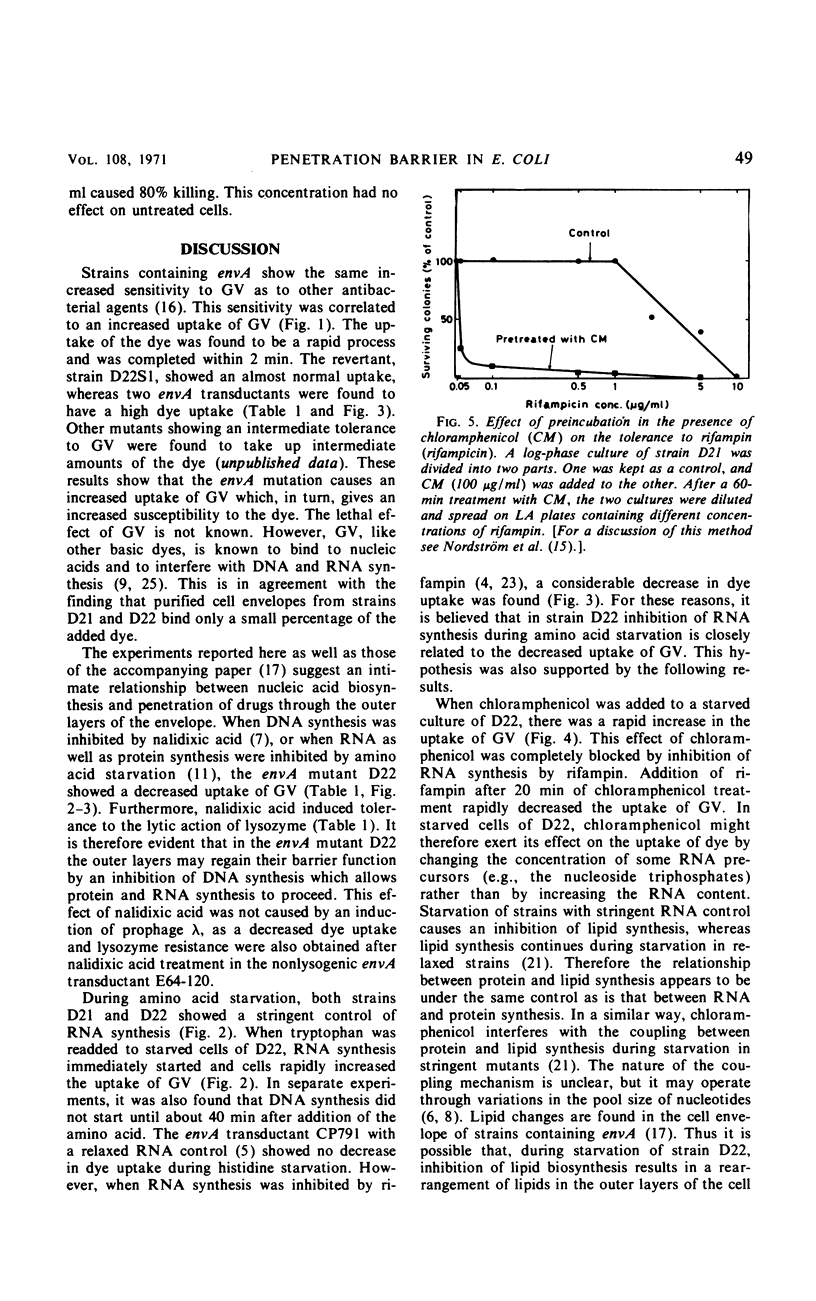
The envA mutation in Escherichia coli K-12, which maps at 1.5 min, was previously shown to mediate sensitivity to gentian violet as well as to several antibiotics. Moreover, strains containing the envA gene were recently found to be lysed by lysozyme in the absence of ethylenediaminetetraacetate. It is here reported that the envA mutation mediates an increased uptake of gentian violet. The uptake of the dye was markedly affected by growth with different antibiotics interfering with macromolecular synthesis. Amino acid starvation of a strain containing envA with a stringent control of ribonucleic acid (RNA) synthesis resulted in a decreased uptake of gentian violet. However, no decrease in dye uptake was found during starvation in an envA transductant with a relaxed control of RNA synthesis. Inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis by nalidixic acid decreased the uptake of gentian violet of envA cells and, in addition, rendered the cells insensitive to the lytic action of lysozyme. Chloramphenicol treatment increased penetrability in wild-type and starved envA cells. In most instances, this effect of chloramphenicol was prevented by selectively interfering with DNA or RNA synthesis. A coordinate regulation of nucleic acid synthesis and penetrability is suggested.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARONSON A. I., SPIEGELMAN S. On the nature of the ribonucleic acid synthesized in the presence of chloramphenicol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 14;53:84–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90796-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTANI G. Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1951 Sep;62(3):293–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.3.293-300.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Eriksson-Grennberg K. G., Normark S., Matsson E. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. IV. Genetic study of mutants resistant to D,L-ampicillin concentrations o 100 mu-g-ml. Genet Res. 1968 Oct;12(2):169–185. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekiel D. H., Hutchins J. E. Mutations affecting RNA polymerase associated with rifampicin resistance in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1968 Oct 19;220(5164):276–277. doi: 10.1038/220276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiil N., Friesen J. D. Isolation of "relaxed" mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):729–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.729-731.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSS W. A., DEITZ W. H., COOK T. M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF NALIDIXIC ACID ON ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1112–1118. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1112-1118.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant J., Harada B. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. 3. The functional relationship between purine ribonucleoside triphosphate pool sizes and the rate of ribonucleic acid accumulation. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3125–3132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irr J., Gallant J. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. II. Stringent control of energy metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2233–2239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner D. J., Khan S. R. Proflavine Uptake and Release in Sensitive and Resistant Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1103–1114. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1103-1114.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzura H., Broda P. Sensitization of Escherichia coli to actinomycin D by the arrest of protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1877–1879. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1877-1879.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H. Acriflavine-binding capacity of Escherichia coli in relation to acriflavine sensitivity and metabolic activity. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1447–1452. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1447-1452.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H. Genetic determination of resistance to acriflavine, phenethyl alcohol, and sodium dodecyl sulfate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):987–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.987-996.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Eriksson-Grennberg K. G., Boman H. G. Resistance of Escherichia coli to penicillins. 3. AmpB, a locus affecting episomally and chromosomally mediated resistance to ampicillin and chlorampheincol. Genet Res. 1968 Oct;12(2):157–168. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Boman H. G., Matsson E. Mutant of Escherichia coli with anomalous cell division and ability to decrease episomally and chromosomally mediated resistance to ampicillin and several other antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1334–1342. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1334-1342.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S. Genetics of a chain-forming mutant of Escherichia coli. Transduction and dominance of the envA gene mediating increased penetration to some antibacterial agents. Genet Res. 1970 Aug;16(1):63–78. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300002287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S. Phenethyl alcohol as a suppressor of the envA phenotype associated with the envA gene in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):51–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.51-58.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokawa Y., Nakao E., Kaziro Y. On the nature of the control by RC gene in e. coli: amino acid-dependent control of lipid synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Oct 10;33(1):108–112. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90263-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino Y. Mutants of Escherichia coli sensitive to methylene blue and acridines. Genet Res. 1966 Feb;7(1):1–11. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300009423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocchini-Valentini G. P., Marino P., Colvill A. J. Mutant of E. coli containing an altered DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Nature. 1968 Oct 19;220(5164):275–276. doi: 10.1038/220275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITKIN E. M. Modification of mutagenesis initiated by ultraviolet light through postteatment of bacteria with basic dyes. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1961 Dec;58(3):135–144. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030580413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


