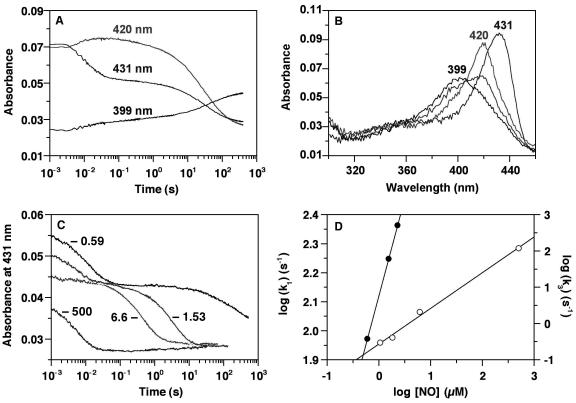
Figure 2.
Stopped-flow analysis of NO binding to heterodimeric sGC. (A) All concentrations are postmixing. sGC (0.6 μM) and NO (0.57 μM) were mixed anaerobically in a stopped-flow spectrophotometer (Hi-Tech Scientific, Salisbury, U.K.) at 4°C. Absorbance changes at 399, 420, and 431 nm are shown. (B) Spectra are shown of the ferrous sGC recorded before the reaction with NO (λSoret at 431 nm), of the 6-coordinate NO complex intermediate immediately after mixing sGC with NO (λSoret at 420 nm), and of the 5-coordinate NO complex recorded 5 min after initiating the reaction (λSoret at 399 nm). A spectrum of a mixture of 6- and 5-coordinate NO complexes during conversion to the 5-coordinate NO complex is shown and also shows the isosbestic point at 406 nm. The sGC concentration was 0.6 μM, and the NO concentration was 0.57 μM. Spectra were recorded at 200 nm/s. (C) The effect of NO concentration on the overall reaction was examined as follows: sGC (0.47 μM) was mixed anaerobically with 0.59, 1.53, 2.28 (data not shown for clarity), 6.6, and 500 μM NO at 4°C, and absorbance changes at 431 nm are shown. (D) The data in C were fit to three consecutive exponential processes. kobs obtained from the first phase (k1), which represents NO binding to sGC heme (filled circles), and that for the third phase (k3), which represents conversion of the 6- to the 5-coordinate ferrous-NO complex (open circles), are plotted against the NO concentration. For the k3 points, the NO concentrations were corrected by the amount that is bound to the heme in the first phase: i.e., the sGC concentration.