Abstract
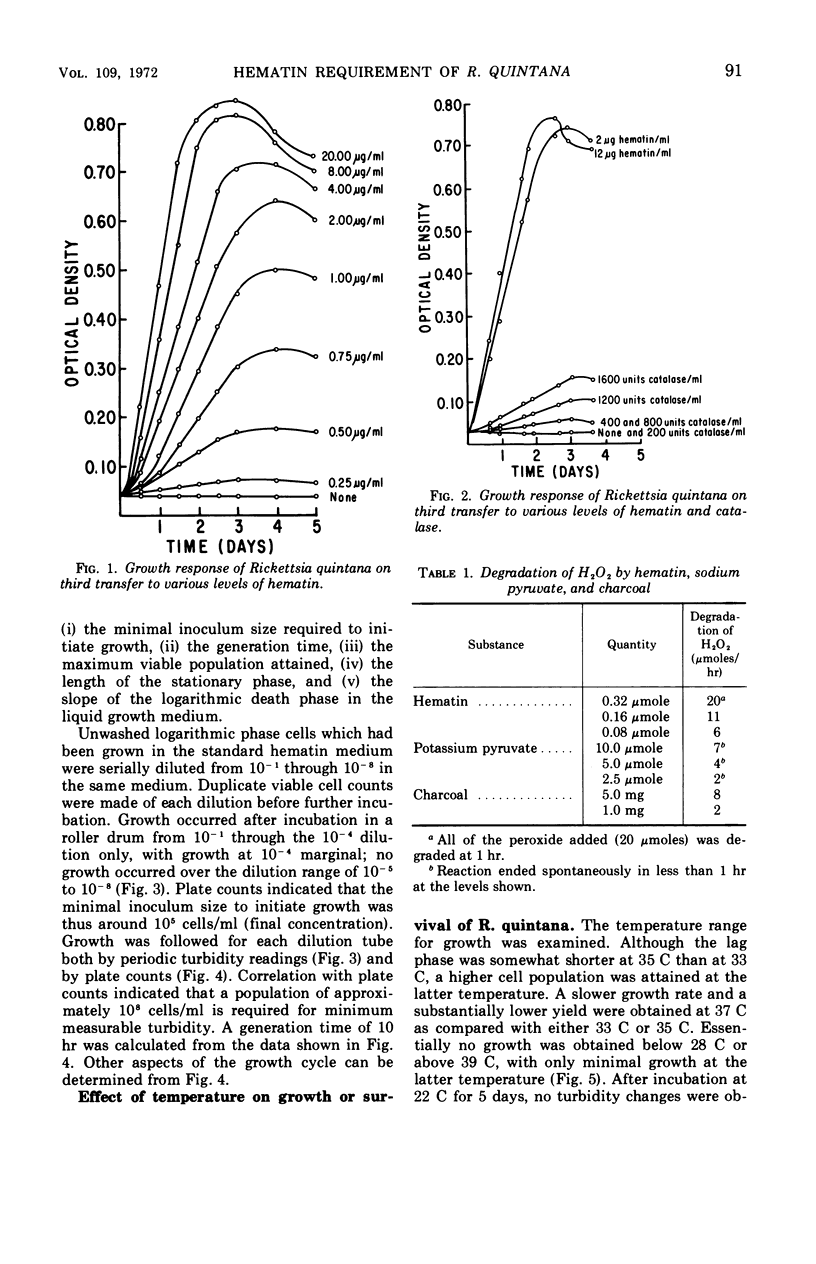
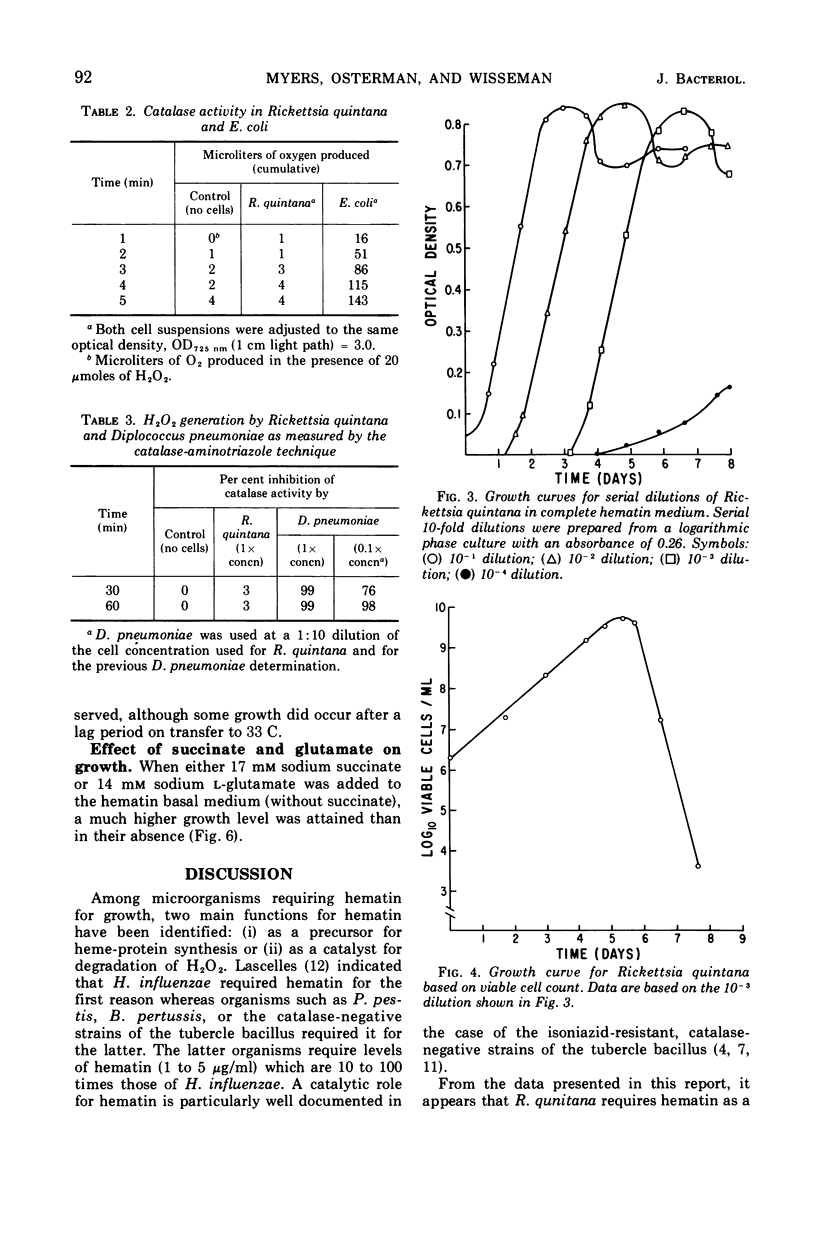
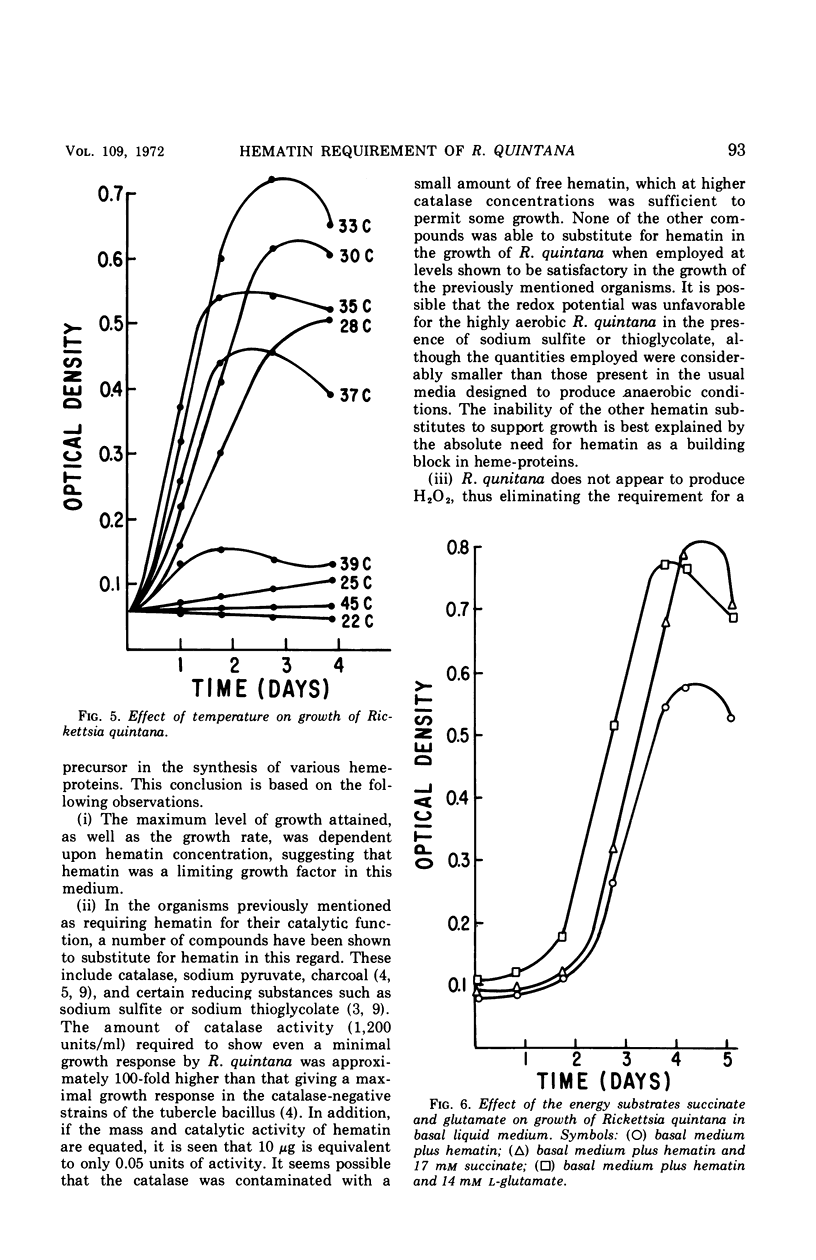
Rickettsia quintana grew in a liquid medium consisting of a brain-heart infusion base supplemented with starch and hematin. The growth requirement for hematin could not be substituted by compounds of known catalytic activity for H2O2, viz., catalase, potassium pyruvate, or charcoal, or by the reducing compounds sodium sulfite and sodium thioglycollate. R. quintana was catalase-negative, but no H2O2 production could be demonstrated by the catalase-aminotriazole technique. A minimum inoculum giving 105 cells/ml was required to initiate growth. The generation time at 33 C was 10 hr. The temperature range for growth was 28 to 37 C. Growth was enhanced when succinate or glutamate was added as energy source.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEERS R. F., Jr, SIZER I. W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOZEMAN F. M., HOPPS H. E., DANAUSKAS J. X., JACKSON E. B., SMADEL J. E. Study on the growth of Rickettsiae. I. A tissue culture system for quantitative estimations of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. J Immunol. 1956 Jun;76(6):475–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN M. L., KOVITZ C., ODA U., MIDDLEBROOK G. Studies on isoniazid and tubercle bacilli. II. The growth requirements, catalase activities, and pathogenic properties of isoniazid-resistant mutants. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Oct;70(4):641–664. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.70.4.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G., Somerson N. L. Catalase-aminotriazole method for measuring secretion of hydrogen peroxide by microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):543–546. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.543-546.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER M. W. Hemin as a growth factor for certain isoniazid-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 May;69(5):797–805. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.69.5.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. Y. Metabolic Activity of the Trench Fever Rickettsia, Rickettsia quintana. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):853–859. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.853-859.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOX R. Haemin and isoniazid resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Apr;12(2):191–202. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-2-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. A. Propagation and growth cycle of Rickettsia quintana in a new liquid medium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):184–190. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.184-190.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers W. F., Cutler L. D., Wisseman C. L., Jr Role of erythrocytes and serum in the nutrition of Rickettsia quintana. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):663–666. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.663-666.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOENNER H. G., LACKMAN D. B., BELL E. J. Factors affecting the growth of rickettsias of the spotted fever group in fertile hens' eggs. J Infect Dis. 1962 Mar-Apr;110:121–128. doi: 10.1093/infdis/110.2.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson J. W. In vitro cultivation of the rickettsial agent of trench fever. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;35(2):155–164. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


