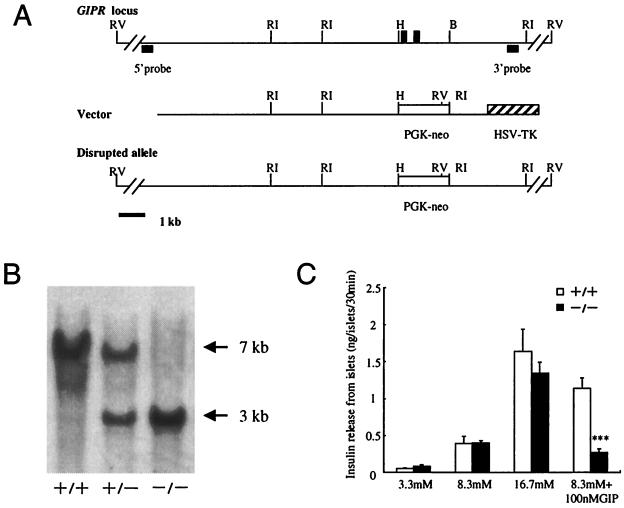
Figure 1.
Disruption of the GIPR gene by homologous recombination. (A) Schematic drawings of the wild-type GIPR locus, the targeting vector, and the mutant allele generated after homologous recombination. Exons 4 and 5 of GIPR are indicated by closed boxes. The 5′ and 3′ probes for DNA blotting are indicated. Restriction enzymes: B, BglII; H, HindIII; RI, EcoRI; RV, EcoRV. PGK-neo, phosphoglycerate kinase-neomycin; HSV-TK, herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase. (B) EcoRI-digested genomic DNA from a litter derived from a GIPR+/− intercross was hybridized with a 3′ probe. The sizes of wild-type (7 kb) and targeted (3 kb) alleles are indicated. (C) Insulin secretion from isolated pancreatic islets was examined in response to the indicated concentrations of glucose with or without 100 nM GIP. Data were obtained from 12-week-old mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SE. ***, P < 0.001 for GIPR−/− mice vs. GIPR+/+.