FIG. 1.
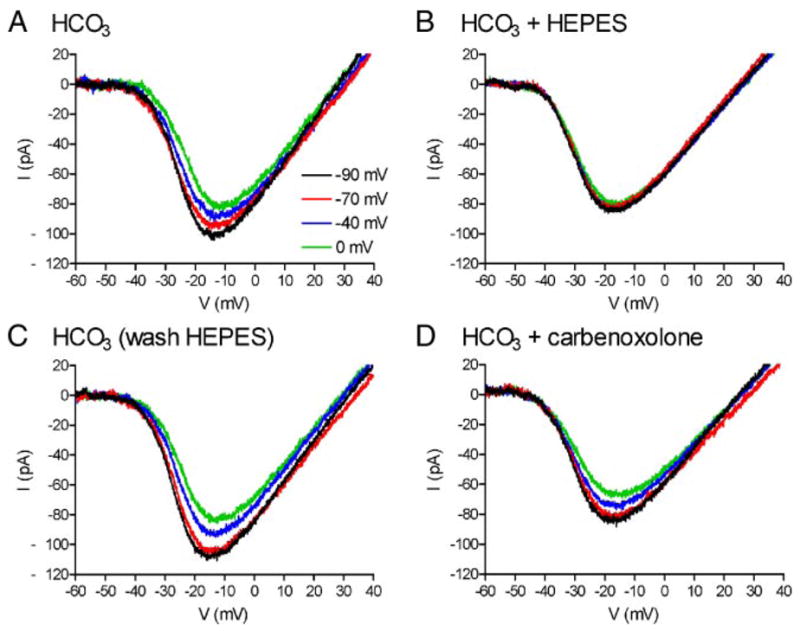
Changes in horizontal cell (HC) membrane potential alter the amplitude and voltage dependence of ICa in a simultaneously recorded cone; these effects are blocked by application of HEPES but not carbenoxolone. A: cone ICa is progressively diminished and shifted to more positive potentials by voltage clamping the HC at −90, −70, −40, and 0 mV. B: addition of HEPES (10 mM) abolished the voltage shift and amplitude changes produced by HC polarization. C: after removal of HEPES, cone ICa was once again progressively diminished and shifted to more positive potentials by voltage clamping the HC at −90, −70, −40, and 0 mV. D: voltage shift and amplitude changes produced by HC polarization persisted in the presence of carbenoxolone (0.2 mM). pH of all solutions was 7.4.
