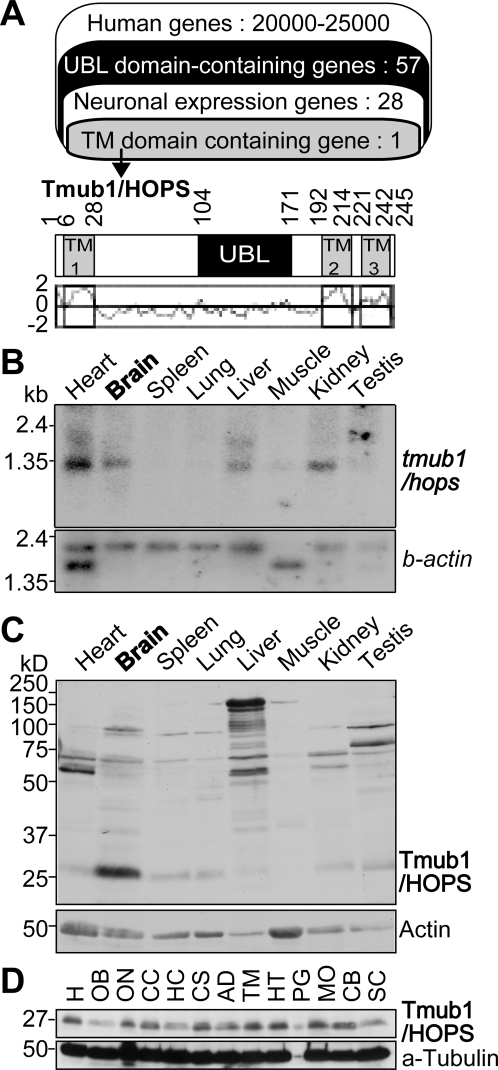
Figure 1. Tmub1/HOPS protein is abundantly expressed in mouse brain.
(A) The summary of the in silico screening (upper panel) and the organization of mouse Tmub1/HOPS (lower panel). Among 20000–25000 human genes from the Celera human genome database, 57 genes contained the UBL domain (black), and 28 of them showed neuronal expression (Table S1). Among them, only one gene, Tmub1/HOPS, had putative TM domains (gray) from SOSUI. Tmub1/HOPS had 3 putative TM domains (TM1–3) and a UBL domain. The hydrophobicity profile of Tmub1/HOPS is shown (under the scheme). The X-axis corresponds to the amino acid sequences and the Y-axis, to its hydrophobicity. Abbreviations: TM, transmembrane. (B) tmub1/hops mRNA expression in mouse tissues. tmub1/hops signals were detected at approximately 1.3 kb in the heart, brain, liver, and kidney. Beta-actin was used as a loading control. (C) Western blotting of mouse tissues with anti-Tmub1/HOPS antibody. The Tmub1/HOPS protein was most abundantly expressed in the brain. The Tmub1/HOPS signals were detected at approximately 26–27 kDa. Actin was used as a loading control. (D) Western blotting of parts of the mouse brain. The Tmub1/HOPS protein was expressed in almost all parts of the mouse brain. Abbreviations: H, homogenate; OB, olfactory bulb; ON, optic nerve; CC, cerebral cortex; HC, hippocampus; CS, corpus striatum; AD, amygdala; TM, thalamus; HT, hypothalamus; PG, pituitary gland; MO, medulla oblongata; CB, cerebellum; SC, spinal cord.