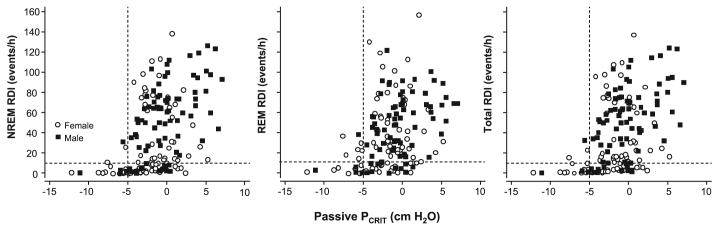
Fig. 4.
Passive Pcrit vs. RDI in all subjects. Sleep apnea prevalence (RDI > 10 events/h; see horizontal dashed line) and severity in non-rapid eye movement (NREM; left), rapid eye movement (REM; middle), and total sleep (right) increased with elevations in passive Pcrit. The presence of sleep apnea and sleep apnea severity increased markedly as passive Pcrit increased above -5 cmH2O (see vertical dashed line), although there was substantial variability (○, women; ■, men).