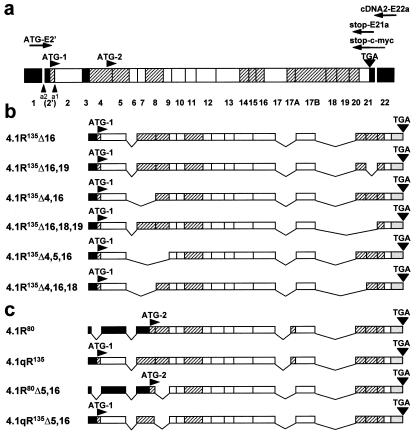
Figure 1.
Cloning of lymphoid HMW protein 4.1R cDNAs. (a) Schematic representation of the exon map of the protein 4.1R. Exons are coded as follows: shaded, alternative; white, constitutive; black, noncoding region. The number of each individual exon is indicated at the bottom. Two translation initiation sites at exons 2′ (ATG-1) and 4 (ATG-2) are indicated, as well as the stop codon (TGA) at exon 21. a1 represents the alternative 3′-splice acceptor site used by LMW 4.1R encoding mRNAs; a2 represents the alternative 3′-splice acceptor site used by HMW 4.1R encoding mRNAs. The primers used for reverse transcription–PCR and for epitope-tagging are indicated: cDNA2-E22a for reverse transcription, ATG-E2′ and stop-E21a for the specific PCR amplification reaction, and ATG-E2′ and stop-c-myc for epitope-tagging. (b) Exon composition of the six cloned HMW 4.1R cDNAs. (c) Exon composition of two nuclear LMW 4.1R protein cDNAs (4.1R80 and 4.1R80Δ5, 16) isolated from MOLT-4 and that of the composite 4.1qR135 and 4.1qR135Δ5,16 cDNA constructs used in this study.